Real-time continuous glucose monitoring significantly reduces severe hypoglycemia in hypoglycemia-unaware patients with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 24103902
- PMCID: PMC3836107
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-0939
Real-time continuous glucose monitoring significantly reduces severe hypoglycemia in hypoglycemia-unaware patients with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) on the frequency of severe hypoglycemia (SH) in patients with established hypoglycemia unawareness.
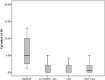
Research design and methods: We conducted a retrospective audit of 35 patients with type 1 diabetes and problematic hypoglycemia unawareness, despite optimized medical therapy (continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion/multiple daily insulin injections), who used CGM for >1 year.
Results: Over a 1-year follow-up period, the median rates of SH were reduced from 4.0 (interquartile range [IQR] 0.75-7.25) episodes/patient-year to 0.0 (0.0-1.25) episodes/patient-year (P < 0.001), and the mean (±SD) rates were reduced from 8.1 ± 13 to 0.6 ± 1.2 episodes/year (P = 0.005). HbA1c was reduced from 8.1 ± 1.2% to 7.6 ± 1.0% over the year (P = 0.005). The mean Gold score, measured in 19 patients, did not change: 5.1 ± 1.5 vs. 5.2 ± 1.9 (P = 0.67).
Conclusions: In a specialist experienced insulin pump center, in carefully selected patients, CGM reduced SH while improving HbA1c but failed to restore hypoglycemia awareness.
Figures
References
-
- Tamborlane WV, Beck RW, Bode BW, et al. Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group Continuous glucose monitoring and intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1464–1476 - PubMed
-
- Choudhary P, Geddes J, Freeman JV, Emery CJ, Heller SR, Frier BM. Frequency of biochemical hypoglycaemia in adults with type 1 diabetes with and without impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia: no identifiable differences using continuous glucose monitoring. Diabet Med 2010;27:666–672 - PubMed
-
- Gold AE, MacLeod KM, Frier BM. Frequency of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type I diabetes with impaired awareness of hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 1994;17:697–703 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical