Alcohol and sexual risk reduction interventions among people living in Russia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24104461
- PMCID: PMC3981957
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-013-0615-9
Alcohol and sexual risk reduction interventions among people living in Russia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
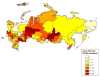
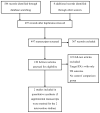
Russia has one of the highest rates of alcohol consumption and is experiencing one of the fastest-growing HIV epidemics in the world. Given these co-occurring health problems, we systematically reviewed combined alcohol and sexual risk interventions to reduce HIV among Russians. We completed comprehensive electronic searches to locate studies that (a) sampled people living in Russia, (b) used a behavioral intervention, and (c) assessed both alcohol and sexual risk behavior. These searches yielded 584 studies, of these, two were included. Compared with controls, intervention participants reported increasing their condom use (ds ranged from 0.12 to 0.85). Within-group improvements in sexual behaviors were found for both groups (ds ranged from 0.19 to 1.94); participants reported fewer sexual partners, more condom use, and reduced alcohol or drug use before sex. These findings support the need and potential benefits for alcohol and HIV interventions among Russians, and suggest directions for public policy.
Figures
References
-
- Grisin SA, Wallander CA. [Accessed May 2, 2013];Russia HIV/AIDS Crisis: Confronting the Present and Facing the Future Center for Strategic and International Studies. 2002 Available at: http://csis.org/files/media/csis/pubs/hiv.pdf.
-
- UNAIDS. [Accessed May 2, 2013];Report on the global AIDS epidemic. 2012 Available at: http://www.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/epidemiolo....
-
- Amirkhanian YA, Tiunov DV, Kelly JA. Risk Factors for HIV and Other Sexually Transmitted Diseases Among Adolescents in St. Petersburg, Russia. Family Planning Perspectives. 2001;33(3):106–12. - PubMed
-
- Rhodes T, Ball A, Stimson GV, Kobyshcha Y, Fitch C, Pokrovsky V, et al. HIV infection associated with drug injecting in the newly independent states, eastern Europe: the social and economic context of epidemics. Addiction. 1999 Sep;94(9):1323–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

