Identification and function of long non-coding RNA
- PMID: 24106460
- PMCID: PMC3788346
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00168
Identification and function of long non-coding RNA
Abstract
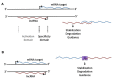
Long non-coding (lnc) RNAs are defined as non-protein coding RNAs distinct from housekeeping RNAs such as tRNAs, rRNAs, and snRNAs, and independent from small RNAs with specific molecular processing machinery such as micro- or piwi-RNAs. Recent studies of lncRNAs across different species have revealed a diverse population of RNA molecules of differing size and function. RNA sequencing studies suggest transcription throughout the genome, so there is a need to understand how sequence relates to functional and structural relationships amongst RNA molecules. Our synthesis of recent studies suggests that neither size, presence of a poly-A tail, splicing, direction of transcription, nor strand specificity are of importance to lncRNA function. Rather, relative genomic position in relation to a target is fundamentally important. In this review, we describe issues of key importance in functional assessment of lncRNA and how this might apply to lncRNAs important in neurodevelopment.
Keywords: epigenetics; gene regulation; neurodevelopment; non-coding RNA.
Figures
References
-
- Barry G., Briggs J. A., Vanichkina D. P., Poth E. M., Beveridge N. J., Ratnu V. S., et al. (2013). The long non-coding RNA Gomafu is acutely regulated in response to neuronal activation and involved in schizophrenia-associated alternative splicing. Mol. Psychiatry 10.1038/mp.2013.45 [Epub ahead of print]. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

