A regenerative approach to the treatment of multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 24107995
- PMCID: PMC4431622
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12647
A regenerative approach to the treatment of multiple sclerosis
Abstract
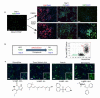
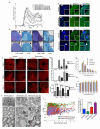
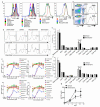
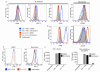
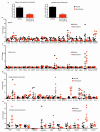
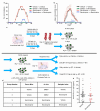
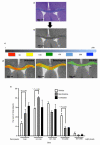
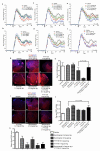
Progressive phases of multiple sclerosis are associated with inhibited differentiation of the progenitor cell population that generates the mature oligodendrocytes required for remyelination and disease remission. To identify selective inducers of oligodendrocyte differentiation, we performed an image-based screen for myelin basic protein (MBP) expression using primary rat optic-nerve-derived progenitor cells. Here we show that among the most effective compounds identifed was benztropine, which significantly decreases clinical severity in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis when administered alone or in combination with approved immunosuppressive treatments for multiple sclerosis. Evidence from a cuprizone-induced model of demyelination, in vitro and in vivo T-cell assays and EAE adoptive transfer experiments indicated that the observed efficacy of this drug results directly from an enhancement of remyelination rather than immune suppression. Pharmacological studies indicate that benztropine functions by a mechanism that involves direct antagonism of M1 and/or M3 muscarinic receptors. These studies should facilitate the development of effective new therapies for the treatment of multiple sclerosis that complement established immunosuppressive approaches.
Figures





Comment in
-
Multiple sclerosis: An old drug plays a new trick.Nature. 2013 Oct 17;502(7471):314-5. doi: 10.1038/nature12694. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24107991 No abstract available.
-
Multiple sclerosis: Drug-enhanced remyelination in a multiple sclerosis model.Nat Rev Neurol. 2013 Dec;9(12):660. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.225. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013. PMID: 24189699 No abstract available.
-
Autoimmune disease: Parkinson's drug promotes myelin repair.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Dec;12(12):905. doi: 10.1038/nrd4181. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 24232375 No abstract available.
-
The best basic science paper in MS in 2013: Antimuscarinic therapies in remyelination.Mult Scler. 2014 Dec;20(14):1814-6. doi: 10.1177/1352458514558679. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Mult Scler. 2014. PMID: 25392329 No abstract available.
References
-
- Franklin RJ, Ffrench-Constant C. Remyelination in the CNS: from biology to therapy. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2008;9:839–855. - PubMed
-
- Franklin RJ. Why does remyelination fail in multiple sclerosis? Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2002;3:705–714. - PubMed
-
- Nunes MC, et al. Identification and isolation of multipotential neural progenitor cells from the subcortical white matter of the adult human brain. Nature Med. 2003;9:439–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

