A distinct subpopulation of human NK cells restricts B cell transformation by EBV
- PMID: 24108698
- PMCID: PMC3833632
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301046
A distinct subpopulation of human NK cells restricts B cell transformation by EBV
Abstract
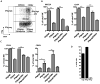
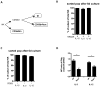
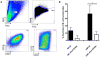
NK cells constitute the first line of defense against pathogens and transformed cells. They mature in secondary lymphoid organs, including tonsils, where common pathogens, such as EBV, enter the host and potentially imprint differentiating cells, which then patrol the body via the blood stream. Therefore, we set out to characterize a distinct human NK cell population in tonsils that produces high amounts of the immunomodulatory and antiviral cytokine IFN-γ. We found that the tonsilar IFN-γ(high) NK cell subset is CD56(bright)NKG2A(+)CD94(+)CD54(+)CD62L(-), is present in tonsils ex vivo and is more mature than other CD56(bright) NK cells in tonsils and less mature than other NK cells in blood, shows very low plasticity even after prolonged cytokine stimulation, accumulates in tonsils of EBV carriers, and is able to potently restrict EBV-induced transformation of B cells. Thus, we characterized a distinct and stable IFN-γ(high) NK cell subpopulation that can specifically restrict malignant transformation of EBV-infected B cells. This subset should be exploited for future development of cell-based therapeutic approaches in EBV-associated malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare not conflict of interest with the presented study.
Figures

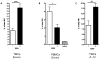
References
-
- Kiessling R, Klein E, Wigzell H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975;5:112–117. - PubMed
-
- Herberman RB, Nunn ME, Lavrin DH. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic acid allogeneic tumors. I. Distribution of reactivity and specificity. Int J Cancer. 1975;16:216–229. - PubMed
-
- Fehniger TA, Cooper MA, Nuovo GJ, Cella M, Facchetti F, Colonna M, Caligiuri MA. CD56bright Natural Killer Cells are Present in Human Lymph Nodes and are Activated by T cell Derived IL-2: a Potential New Link between Adaptive and Innate Immunity. Blood. 2003;102:3052–3057. - PubMed
-
- Ferlazzo G, Thomas D, Lin SL, Goodman K, Morandi B, Muller WA, Moretta A, Münz C. The abundant NK cells in human lymphoid tissues require activation to express killer cell Ig-like receptors and become cytolytic. Journal of Immunology. 2004;172:1455–1462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

