Relationship between 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate concentration and spontaneous preterm birth
- PMID: 24113254
- PMCID: PMC3926421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2013.10.008
Relationship between 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate concentration and spontaneous preterm birth
Abstract
Objective: 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate 250 mg weekly reduces recurrent spontaneous preterm birth in women with a prior spontaneous preterm birth by 33%. The dose is not based on pharmacologic considerations. A therapeutic concentration has not been determined hampering any attempt to optimize treatment. This study evaluated the relationship between 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate plasma concentrations and the rate of spontaneous preterm birth in women with singleton gestation.
Study design: A single blood sample was obtained between 25 and 28 weeks' gestation from 315 women with a spontaneous preterm birth who participated in a placebo-controlled, prospective, randomized clinical trial evaluating the benefit of omega-3 supplementation in reducing preterm birth. All women in the parent study received 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate and 434 received omega-3 supplementation and 418 received a placebo. Plasma from 315 consenting women was analyzed for 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate concentration.
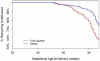
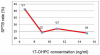
Results: There were no differences between placebo and omega-3 supplemented groups in demographic variables, outcomes or in mean 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate concentration. Plasma concentrations of 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate ranged from 3.7-56 ng/mL. Women with plasma concentrations of 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate in the lowest quartile had a significantly higher risk of spontaneous preterm birth (P = .03) and delivered at significantly earlier gestational ages (P = .002) than did women in the second to fourth quartiles. The lowest preterm birth rates were seen when median 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate concentrations exceeded 6.4 ng/mL.
Conclusion: Low plasma 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate concentration is associated with an increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth. This finding validates efficacy of this treatment but suggests that additional studies are needed to determine the optimal dosage.
Keywords: 17-hydroxyprogesterone caproate concentration-response; dose response; pharmacodynamics.
Copyright © 2014 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Meis PJ, Klebanoff M, Thom E, et al. Prevention of recurrent preterm delivery by 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2379–85. - PubMed
- N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1299. Erratum in:
-
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists ACOG committee opinion no 419: use of progesterone to reduce preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:963–5. - PubMed
-
- [Accessed 4/26/2013]; www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guid....
-
- [Accessed 4/26/2013]; http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformati....
-
- Johnson JW, Austin KL, Jones GS, Davis GH, King TM. Efficacy of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone caproate in the prevention of premature labor. N. Engl J Med. 1975;293:675–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HD36801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027917/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD047905/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD047905/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD047905/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27860/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MO1-RR-000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HD21410/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027860/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27917/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021410/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

