Concurrent granulomatous hepatitis, pneumonitis and sepsis as a complication of intravesical BCG immunotherapy
- PMID: 24114600
- PMCID: PMC3822071
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-200624
Concurrent granulomatous hepatitis, pneumonitis and sepsis as a complication of intravesical BCG immunotherapy
Abstract
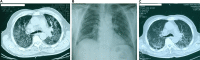
Intravesical administration of BCG is a relatively simple procedure used successfully in the treatment of superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. It is usually well tolerated with few major side effects. The authors report the case of an 80-year-old man who presented with sepsis, jaundice, hepatic and pulmonary failure 10 days after his last BCG instillation therapy, that was attributed to concurrent granulomatous hepatitis and pneumonitis due to Mycobacterium bovis dissemination. In rare instances severe life-threatening complications occur in relation with BCG instillation immunotherapy that may involve multiple organs and have different presentations and require a high index of suspicion and clinical awareness in a wide range of medical specialties.
Figures

References
-
- Alexandroff AB, Jackson AM, O'Donnell MA, et al. BCG immunotherapy of bladder cancer: 20 years on. Lancet 1999;2013:1689–94 - PubMed
-
- Lamm DL. Efficacy and safety of bacilli Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy in superficial bladder cancer. Clin Infect Dis 2000;2013(Suppl 3):S86–90 - PubMed
-
- Koga H, Kuroda M, Kudo S, et al. Adverse drug reactions of intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin instillation and risk factors of the development of adverse drug reactions in superficial cancer and carcinoma in situ of the bladder. Int J Urol 2005;2013:145–51 - PubMed
-
- Lamm DL. Complications of bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy. Urol Clin North Am 1992;2013:565–72 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
