Molecular targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current and future
- PMID: 24115810
- PMCID: PMC3787343
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6144
Molecular targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current and future
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most frequent tumors worldwide. The majority of HCC cases occur in patients with chronic liver disease. Despite regular surveillance to detect small HCC in these patients, HCC is often diagnosed at an advanced stage. Because HCC is highly resistant to conventional systemic therapies, the prognosis for advanced HCC patients remains poor. The introduction of sorafenib as the standard systemic therapy has unveiled a new direction for future research regarding HCC treatment. However, given the limited efficacy of the drug, a need exists to look beyond sorafenib. Many molecular targeted agents that inhibit different pathways involved in hepatocarcinogenesis are under various phases of clinical development, and novel targets are being assessed in HCC. This review aims to summarize the efforts to target molecular components of the signaling pathways that are responsible for the development and progression of HCC and to discuss perspectives on the future direction of research.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Molecular agents; Sorafenib; Targeted therapy.
Figures

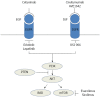
References
-
- Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M, Cléries R. Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S5–S16. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–1917. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Bruix J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology. 2003;37:429–442. - PubMed
-
- Sarker D, Molife R, Evans TR, Hardie M, Marriott C, Butzberger-Zimmerli P, Morrison R, Fox JA, Heise C, Louie S, et al. A phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of TKI258, an oral, multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2075–2081. - PubMed
-
- Brechot C, Pourcel C, Louise A, Rain B, Tiollais P. Presence of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in cellular DNA of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1980;286:533–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

