Remote measurements of heart and respiration rates for telemedicine
- PMID: 24115996
- PMCID: PMC3792902
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071384
Remote measurements of heart and respiration rates for telemedicine
Abstract
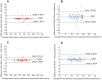
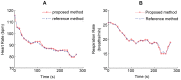
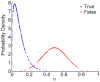
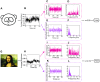
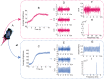
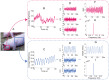
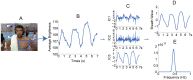
Non-contact and low-cost measurements of heart and respiration rates are highly desirable for telemedicine. Here, we describe a novel technique to extract blood volume pulse and respiratory wave from a single channel images captured by a video camera for both day and night conditions. The principle of our technique is to uncover the temporal dynamics of heart beat and breathing rate through delay-coordinate transformation and independent component analysis-based deconstruction of the single channel images. Our method further achieves robust elimination of false positives via applying ratio-variation probability distributions filtering approaches. Moreover, it enables a much needed low-cost means for preventing sudden infant death syndrome in new born infants and detecting stroke and heart attack in elderly population in home environments. This noncontact-based method can also be applied to a variety of animal model organisms for biomedical research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Stiedl O, Spiess J (1997) Effect of tone-dependent fear conditioning on heart rate and behavior of C57BL/6N mice. Behav Neurosci 111: 703–711. - PubMed
-
- Stiedl O, Tovote P, Ögren SO, Meyer M (2004) Behavioral and autonomic dynamics during contextual fear conditioning in mice. Auton Neurosci 115: 15–27. - PubMed
-
- Stiedl O, Jansen RF, Pieneman AW, Ögren SO, Meyer M (2009) Assessing aversive emotional states through the heart in mice: Implications for cardiovascular dysregulation in affective disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33: 181–190. - PubMed
-
- Steinschneider A (1972) Prolonged apnea and the sudden infant death syndrome: clinical and laboratory observations. Pediatrics 50: 646–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

