Bacterial community mapping of the mouse gastrointestinal tract
- PMID: 24116019
- PMCID: PMC3792069
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074957
Bacterial community mapping of the mouse gastrointestinal tract
Abstract
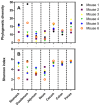
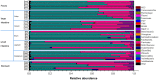
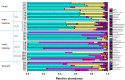
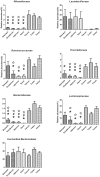
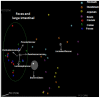
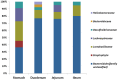
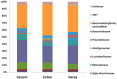
Keeping mammalian gastrointestinal (GI) tract communities in balance is crucial for host health maintenance. However, our understanding of microbial communities in the GI tract is still very limited. In this study, samples taken from the GI tracts of C57BL/6 mice were subjected to 16S rRNA gene sequence-based analysis to examine the characteristic bacterial communities along the mouse GI tract, including those present in the stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, colon and feces. Further analyses of the 283,234 valid sequences obtained from pyrosequencing revealed that the gastric, duodenal, large intestinal and fecal samples had higher phylogenetic diversity than the jejunum and ileum samples did. The microbial communities found in the small intestine and stomach were different from those seen in the large intestine and fecal samples. A greater proportion of Lactobacillaceae were found in the stomach and small intestine, while a larger proportion of anaerobes such as Bacteroidaceae, Prevotellaceae, Rikenellaceae, Lachnospiraceae, and Ruminococcaceae were found in the large intestine and feces. In addition, inter-mouse variations of microbiota were observed between the large intestinal and fecal samples, which were much smaller than those between the gastric and small intestinal samples. As far as we can ascertain, ours is the first study to systematically characterize bacterial communities from the GI tracts of C57BL/6 mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2005) Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 307: 1915–1920. - PubMed
-
- Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM, et al. (2008) Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 57: 1470–1481. - PubMed
-
- Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444: 1022–1023. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

