Cyclic peptides as therapeutic agents and biochemical tools
- PMID: 24116270
- PMCID: PMC3792197
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2012.20.1.019
Cyclic peptides as therapeutic agents and biochemical tools
Abstract
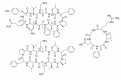
There are many cyclic peptides with diverse biological activities, such as antibacterial activity, immunosuppressive activity, and anti-tumor activity, and so on. Encouraged by natural cyclic peptides with biological activity, efforts have been made to develop cyclic peptides with both genetic and synthetic methods. The genetic methods include phage display, intein-based cyclic peptides, and mRNA display. The synthetic methods involve individual synthesis, parallel synthesis, as well as split-and-pool synthesis. Recent development of cyclic peptide library based on split-and-pool synthesis allows on-bead screening, in-solution screening, and microarray screening of cyclic peptides for biological activity. Cyclic peptides will be useful as receptor agonist/antagonist, RNA binding molecule, enzyme inhibitor and so on, and more cyclic peptides will emerge as therapeutic agents and biochemical tools.
Keywords: Cyclic peptides; Drug lead; On-bead screening; Split-and-pool synthesis.
Figures
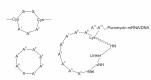

References
-
- Athanassiou Z. Dias R. L. Moehle K. Dobson N. Varani G. Robinson J. A. Structural mimicry of retroviral tat proteins by constrained beta-hairpin peptidomimetics: ligands with high affinity and selectivity for viral TAR RNA regulatory elements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2004);126:6906–6913. doi: 10.1021/ja0497680. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

