TEC and MAPK Kinase Signalling Pathways in T helper (TH) cell Development, TH2 Differentiation and Allergic Asthma
- PMID: 24116341
- PMCID: PMC3792371
- DOI: 10.4172/2155-9899.S12-011
TEC and MAPK Kinase Signalling Pathways in T helper (TH) cell Development, TH2 Differentiation and Allergic Asthma
Abstract
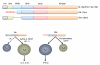
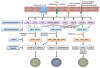
Significant advances in our understanding of the signalling events during T cell development and differentiation have been made in the past few decades. It is clear that ligation of the T cell receptor (TCR) triggers a series of proximal signalling cascades regulated by an array of protein kinases. These orchestrated and highly regulated series of events, with differential requirements of particular kinases, highlight the disparities between αβ+CD4+ T cells. Throughout this review we summarise both new and old studies, highlighting the role of Tec and MAPK in T cell development and differentiation with particular focus on T helper 2 (TH2) cells. Finally, as the allergy epidemic continues, we feature the role played by TH2 cells in the development of allergy and provide a brief update on promising kinase inhibitors that have been tested in vitro, in pre-clinical disease models in vivo and into clinical studies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IL-2-inducible T-cell kinase modulates TH2-mediated allergic airway inflammation by suppressing IFN-γ in naive CD4+ T cells.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Oct;132(4):811-20.e1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.04.033. Epub 2013 Jun 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23768572 Free PMC article.
-
OX40L induces helper T cell differentiation during cell immunity of asthma through PI3K/AKT and P38 MAPK signaling pathway.J Transl Med. 2018 Mar 20;16(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1436-4. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29554934 Free PMC article.
-
Differences between T helper cell type I (Th1) and Th2 cell lines in signalling pathways for induction of contact-dependent T cell help.Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):85-93. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220114. Eur J Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1309700
-
CD4+ T helper 2 cells--microbial triggers, differentiation requirements and effector functions.Immunology. 2011 Dec;134(4):368-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03497.x. Immunology. 2011. PMID: 22043920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
'All things considered': transcriptional regulation of T helper type 2 cell differentiation from precursor to effector activation.Immunology. 2013 Sep;140(1):31-8. doi: 10.1111/imm.12121. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23668241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Febrile temperature change modulates CD4 T cell differentiation via a TRPV channel-regulated Notch-dependent pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 8;117(36):22357-22366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922683117. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32839313 Free PMC article.
-
Equine Herpesvirus 1 Bridles T Lymphocytes To Reach Its Target Organs.J Virol. 2019 Mar 21;93(7):e02098-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02098-18. Print 2019 Apr 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30651370 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese expert consensus on diagnosis and management of severe asthma.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Dec;10(12):7020-7044. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.11.135. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30746249 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Dissecting the Landscape of Activated CMV-Stimulated CD4+ T Cells in Humans by Linking Single-Cell RNA-Seq With T-Cell Receptor Sequencing.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 7;12:779961. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.779961. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34950144 Free PMC article.
-
PDGF induces SphK1 expression via Egr-1 to promote pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):C983-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00059.2016. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27099350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crotty S. Follicular helper CD4 T cells (TFH) Annu Rev Immunol. 2011;29:621–663. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
