Unbiased screening of marine sponge extracts for anti-inflammatory agents combined with chemical genomics identifies girolline as an inhibitor of protein synthesis
- PMID: 24117378
- PMCID: PMC4371607
- DOI: 10.1021/cb400740c
Unbiased screening of marine sponge extracts for anti-inflammatory agents combined with chemical genomics identifies girolline as an inhibitor of protein synthesis
Abstract
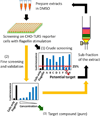
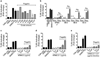
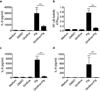
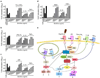
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a critical role in innate immunity, but activation of TLR signaling pathways is also associated with many harmful inflammatory diseases. Identification of novel anti-inflammatory molecules targeting TLR signaling pathways is central to the development of new treatment approaches for acute and chronic inflammation. We performed high-throughput screening from crude marine sponge extracts on TLR5 signaling and identified girolline. We demonstrated that girolline inhibits signaling through both MyD88-dependent and -independent TLRs (i.e., TLR2, 3, 4, 5, and 7) and reduces cytokine (IL-6 and IL-8) production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and macrophages. Using a chemical genomics approach, we identified Elongation Factor 2 as the molecular target of girolline, which inhibits protein synthesis at the elongation step. Together these data identify the sponge natural product girolline as a potential anti-inflammatory agent acting through inhibition of protein synthesis.
Figures


References
-
- Palm NW, Medzhitov R. Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev. 2009;227:221–233. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:805–820. - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA. The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell. 1996;86:973–983. - PubMed
-
- Moresco EM, LaVine D, Beutler B. Toll-like receptors. Curr Biol. 2011;21:R488–R493. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat.Immunol. 2010;11:373–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

