Yersinia pseudotuberculosis uses Ail and YadA to circumvent neutrophils by directing Yop translocation during lung infection
- PMID: 24119087
- PMCID: PMC3981955
- DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12219
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis uses Ail and YadA to circumvent neutrophils by directing Yop translocation during lung infection
Abstract
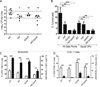
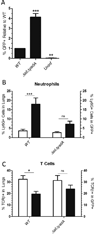
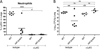
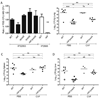
A Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (Yptb) murine model of lung infection was previously developed using the serotype III IP2666NdeI strain, which robustly colonized lungs but only sporadically disseminated to the spleen and liver. We demonstrate here that a serotype Ib Yptb strain, IP32953, colonizes the lungs at higher levels and disseminates more efficiently to the spleen and liver compared with IP2666NdeI . The role of adhesins was investigated during IP32953 lung infection by constructing isogenic Δail, Δinv, ΔpsaE and ΔyadA mutants. An IP32953ΔailΔyadA mutant initially colonized but failed to persist in the lungs and disseminate to the spleen and liver. Yptb expressing these adhesins selectively bound to and targeted neutrophils for translocation of Yops. This selective targeting was critical for virulence because persistence of the ΔailΔyadA mutant was restored following intranasal infection of neutropenic mice. Furthermore, Ail and YadA prevented killing by complement-mediated mechanisms during dissemination to and/or growth in the spleen and liver, but not in the lungs. Combined, these results demonstratethat Ail and YadA are critical, redundant virulence factors during lung infection, because they thwart neutrophils by directing Yop-translocation specifically into these cells.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Unraveling neutrophil- Yersinia interactions during tissue infection.F1000Res. 2019 Jul 11;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-1046. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.18940.1. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 31327994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Yersinia pestis Ail protein mediates binding and Yop delivery to host cells required for plague virulence.Infect Immun. 2009 Feb;77(2):825-36. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00913-08. Epub 2008 Dec 8. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19064637 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal inoculation of mice with Yersinia pseudotuberculosis causes a lethal lung infection that is dependent on Yersinia outer proteins and PhoP.Infect Immun. 2007 Jan;75(1):429-42. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01287-06. Epub 2006 Oct 30. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17074849 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesins and host serum factors drive Yop translocation by yersinia into professional phagocytes during animal infection.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(6):e1003415. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003415. Epub 2013 Jun 20. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23818844 Free PMC article.
-
Yersinia adhesin A (YadA)--beauty & beast.Int J Med Microbiol. 2015 Feb;305(2):252-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.12.008. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Int J Med Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25604505 Review.
Cited by
-
Fis Is Essential for Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Virulence and Protects against Reactive Oxygen Species Produced by Phagocytic Cells during Infection.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Sep 30;12(9):e1005898. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005898. eCollection 2016 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27689357 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Virulence Plasmid in Pathogen-Phagocyte Interactions in Mesenteric Lymph Nodes.EcoSal Plus. 2021 Dec 15;9(2):eESP00142021. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0014-2021. Epub 2021 Oct 27. EcoSal Plus. 2021. PMID: 34910573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling neutrophil- Yersinia interactions during tissue infection.F1000Res. 2019 Jul 11;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-1046. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.18940.1. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 31327994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of PhoP and intra-species variations on virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis during the natural oral infection route.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 30;9(7):e103541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103541. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25075520 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and Phenotypic Analysis Reveals New Functions for the Tat Pathway in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis.J Bacteriol. 2016 Sep 22;198(20):2876-86. doi: 10.1128/JB.00352-16. Print 2016 Oct 15. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27501981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balada-Llasat JM, Panilaitis B, Kaplan D, Mecsas J. Oral inoculation with Type III secretion mutants of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis provides protection from oral, intraperitoneal, or intranasal challenge with virulent Yersinia. Vaccine. 2007;25:1526–1533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

