Improvement of the quality of BRAF testing in melanomas with nationwide external quality assessment, for the BRAF EQA group
- PMID: 24119386
- PMCID: PMC3852250
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-472
Improvement of the quality of BRAF testing in melanomas with nationwide external quality assessment, for the BRAF EQA group
Abstract
Background: Knowledge about tumour gene mutation status is essential for the treatment of increasing numbers of cancer patients, and testing quality has a major impact on treatment response and cost. In 2012, 4,629 tests for BRAF p.V600 were performed in France, in patients with melanomas.
Methods: Two batches of unstained melanoma sections were sent, in May and November 2012, to the 46 laboratories supported by the French National Institute of Cancer (INCa). An external quality assessment (EQA) evaluated mutation status, response times and compliance with INCa recommendations.
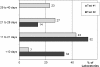
Results: All the French laboratories involved in testing participated in the EQA. Fourteen different methods were used to detect BRAF mutations, most consisting of combinations of in-house techniques. False responses were noted in 25/520 cases (4.8%), 11 of which concerned confusion between p.V600E and p.V600K. Thus, 2.7% of responses would have led to inappropriate treatment. Within six months, mean response times decreased from 22 to 12 days (P<0.001), and the percentage of samples evaluated by a pathologist for tumour cell content increased, from 75.2% to 96.9% (P<0.001).
Conclusion: Despite the use of non-certified methods, the false response rate was low. Nationwide EQA can improve the quality of molecular pathology tests on tumours.
Figures

References
-
- Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Láng I, Folprecht G, Nowacki MP, Cascinu S, Shchepotin I, Maurel J, Cunningham D, Tejpar S, Schlichting M, Zubel A, Celik I, Rougier P, Ciardiello F. Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(15):2011–2019. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.5091. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lièvre A, Bachet JB, Boige V, Cayre A, Le Corre D, Buc E, Ychou M, Bouché O, Landi B, Louvet C, André T, Bibeau F, Diebold MD, Rougier P, Ducreux M, Tomasic G, Emile JF, Penault-Llorca F, Laurent-Puig P. KRAS mutations as an independent prognostic factor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(3):374–379. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.12.5906. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, Kinoshita I, Fujita Y, Okinaga S, Hirano H, Yoshimori K, Harada T, Ogura T, Ando M, Miyazawa H, Tanaka T, Saijo Y, Hagiwara K, Morita S, Nukiwa T. North-East Japan Study Group. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(25):2380–2388. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0909530. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, Hogg D, Lorigan P, Lebbe C, Jouary T, Schadendorf D, Ribas A, O'Day SJ, Sosman JA, Kirkwood JM, Eggermont AM, Dreno B, Nolop K, Li J, Nelson B, Hou J, Lee RJ, Flaherty KT, McArthur GA. BRIM-3 Study Group. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(26):2507–2516. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1103782. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, Goldhirsch A, Untch M, Smith I, Gianni L, Baselga J, Bell R, Jackisch C, Cameron D, Dowsett M, Barrios CH, Steger G, Huang CS, Andersson M, Inbar M, Lichinitser M, Láng I, Nitz U, Iwata H, Thomssen C, Lohrisch C, Suter TM, Rüschoff J, Suto T, Greatorex V, Ward C, Straehle C, McFadden E. et al.Herceptin Adjuvant (HERA) Trial Study Team. Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(16):1659–72. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052306. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

