The mismatch between the health research and development (R&D) that is needed and the R&D that is undertaken: an overview of the problem, the causes, and solutions
- PMID: 24119660
- PMCID: PMC3796018
- DOI: 10.3402/gha.v6i0.22450
The mismatch between the health research and development (R&D) that is needed and the R&D that is undertaken: an overview of the problem, the causes, and solutions
Abstract
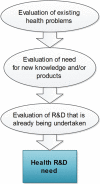
One of the most pressing global health problems is that there is a mismatch between the health research and development (R&D) that is needed and that which is undertaken. The dependence of health R&D on market incentives in the for-profit private sector and the lack of coordination by public and philanthropic funders on global R&D priorities have resulted in a global health R&D landscape that neglects certain products and populations and is characterised, more generally, by a distribution that is not 'needs-driven'. This article provides an overview of the mismatch, its causes, and solutions.
Keywords: R&D; agenda; pharmaceutical industry; priorities; research funding.
Figures

References
-
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Measuring expenditure on health-related R&D; Paris: OECD; 2001.
-
- Frascati manual: proposed standard practice for surveys on research and experimental development. 6th edition. Paris: OECD; 2002. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
-
- G-FINDER. R&D scope document. Available from: http://g-finder.policycures.org/g-finder/registered/docs/help.jsp#OUTOFS... (Excluded from the survey) [cited 2 October 2013]
-
- Commission on Health Research for Development. New York: Oxford University Press; 1990. Health research: essential link to equity in development; p. 157. Available from: http://www.cohred.org/downloads/open_archive/ComReports_0.pdf [cited 2 October 2013]
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2197–223. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
