Macrocytic anemia and mitochondriopathy resulting from a defect in sideroflexin 4
- PMID: 24119684
- PMCID: PMC3824126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.09.011
Macrocytic anemia and mitochondriopathy resulting from a defect in sideroflexin 4
Abstract
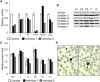
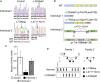
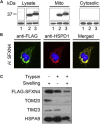
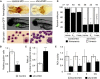
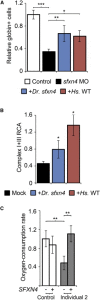
We used exome sequencing to identify mutations in sideroflexin 4 (SFXN4) in two children with mitochondrial disease (the more severe case also presented with macrocytic anemia). SFXN4 is an uncharacterized mitochondrial protein that localizes to the mitochondrial inner membrane. sfxn4 knockdown in zebrafish recapitulated the mitochondrial respiratory defect observed in both individuals and the macrocytic anemia with megaloblastic features of the more severe case. In vitro and in vivo complementation studies with fibroblasts from the affected individuals and zebrafish demonstrated the requirement of SFXN4 for mitochondrial respiratory homeostasis and erythropoiesis. Our findings establish mutations in SFXN4 as a cause of mitochondriopathy and macrocytic anemia.
Copyright © 2013 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Vafai S.B., Mootha V.K. Mitochondrial disorders as windows into an ancient organelle. Nature. 2012;491:374–383. - PubMed
-
- DiMauro S., Servidei S., Zeviani M., DiRocco M., DeVivo D.C., DiDonato S., Uziel G., Berry K., Hoganson G., Johnsen S.D. Cytochrome c oxidase deficiency in Leigh syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1987;22:498–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

