Glial influence on the blood brain barrier
- PMID: 24123158
- PMCID: PMC4068281
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.22575
Glial influence on the blood brain barrier
Abstract
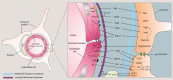
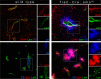
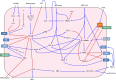
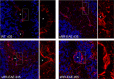
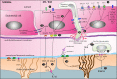
The Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) is a specialized vascular structure tightly regulating central nervous system (CNS) homeostasis. Endothelial cells are the central component of the BBB and control of their barrier phenotype resides on astrocytes and pericytes. Interactions between these cells and the endothelium promote and maintain many of the physiological and metabolic characteristics that are unique to the BBB. In this review we describe recent findings related to the involvement of astroglial cells, including radial glial cells, in the induction of barrier properties during embryogenesis and adulthood. In addition, we describe changes that occur in astrocytes and endothelial cells during injury and inflammation with a particular emphasis on alterations of the BBB phenotype.
Keywords: BBB; astrocyte; astrogliosis; glial; multiple sclerosis.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Adams RH. Vascular patterning by Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and ephrins. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13:55–60. - PubMed
-
- Adner M, Jansen I, Edvinsson L. Endothelin-A receptors mediate contraction in human cerebral, meningeal and temporal arteries. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1994;49(Suppl):S117–S121. - PubMed
-
- Albanese C, Wu K, D'Amico M, Jarrett C, Joyce D, Hughes J, Hulit J, Sakamaki T, Fu M, Ben-Ze'ev A, Bromberg JF, Lamberti C, Verma U, Gaynor RB, Byers SW, Pestell RG. IKKalpha regulates mitogenic signaling through transcriptional induction of cyclin D1 via Tcf. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14:585–599. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

