Visual performance after the implantation of a new trifocal intraocular lens
- PMID: 24124348
- PMCID: PMC3794849
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S44415
Visual performance after the implantation of a new trifocal intraocular lens
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the subjective and objective visual results after the implantation of a new trifocal diffractive intraocular lens.
Methods: A NEW TRIFOCAL DIFFRACTIVE INTRAOCULAR LENS WAS DESIGNED COMBINING TWO SUPERIMPOSED DIFFRACTIVE PROFILES: one with +1.75 diopters (D) addition for intermediate vision and the other with +3.50 D addition for near vision. Fifty eyes of 25 patients that were operated on by one surgeon are included in this study. The uncorrected and best distance-corrected monocular and binocular, near, intermediate, and distance visual acuities, contrast sensitivity, and defocus curves were measured 6 months postoperatively. In addition to the standard clinical follow-up, a questionnaire evaluating individual satisfaction and quality of life was submitted to the patients.
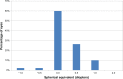
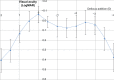
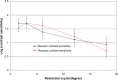
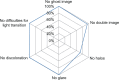
Results: The mean age of patients at the time of surgery was 70 ± 10 years. The mean uncorrected and corrected monocular distance visual acuity (VA) were LogMAR 0.06 ± 0.10 and LogMAR 0.00 ± 0.08, respectively. The outcomes for the binocular uncorrected distance visual acuity were almost the same (LogMAR -0.04 ± 0.09). LogMAR -010 ± 0.15 and 0.02 ± 0.06 were measured for the binocular uncorrected intermediate and near VA, respectively. The distance-corrected visual acuity was maintained in mesopic conditions. The contrast sensitivity was similar to that obtained after implantation of a bifocal intraocular lens and did not decrease in mesopic conditions. The binocular defocus curve confirms good VA even in the intermediate distance range, with a moderate decrease of less than LogMAR 0.2 at -1.5 D, with respect to the best distance VA at 0 D defocus. Patient satisfaction was high. No discrepancy between the objective and subjective outcomes was evidenced.
Conclusion: The introduction of a third focus in diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses improves the intermediate vision with minimal visual discomfort for the patient.
Keywords: diffractive multifocal; lens implantation; third focus; trifocal diffractive intraocular lens.
Figures

References
-
- Mesci C, Erbil H, Ozdoker L, Karakurt Y, Bilge AD. Visual acuity and contrast sensitivity function after accommodative and multifocal intraocular lens implantation. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2010;20(1):90–100. - PubMed
-
- Maxwell WA, Lane SS, Zhou F. Performance of presbyopia-correcting intraocular lenses in distance optical bench tests. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35(1):166–171. - PubMed
-
- Mesci C, Erbil HH, Olgun A, Aydin N, Candemir B, Akçakaya AA. Differences in contrast sensitivity between monofocal, multifocal and accommodating intraocular lenses: long-term results. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2010;38(8):768–777. - PubMed
-
- Petermeier K, Messias A, Gekeler F, Szurman P. Effect of +3.00 diopter and +4.00 diopter additions in multifocal intraocular lenses on defocus profiles, patient satisfaction, and contrast sensitivity. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(4):720–726. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

