Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: radiologic identification of usual interstitial pneumonia pattern
- PMID: 24126367
- PMCID: PMC4228744
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.13130187
Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: radiologic identification of usual interstitial pneumonia pattern
Abstract
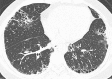
Purpose: To determine the accuracy of computed tomography (CT) in identifying the histopathologic usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD).
Materials and methods: All patients were enrolled into institutional review board-approved longitudinal cohorts at their respective institution, and informed consent was obtained at the time of enrollment. Images of patients with surgical lung biopsy-proved RA-ILD (n = 69) were collected from three tertiary care centers. Two experienced thoracic radiologists independently reviewed the CT scans. The CT pattern was categorized as definite UIP, possible UIP, or inconsistent with UIP in accordance with published criteria. Findings of biopsies were reviewed by an experienced lung pathologist. The sensitivity and specificity of definite CT UIP pattern to histopathologic UIP pattern were determined. The agreement between radiologists was assessed by calculating a κ score.
Results: The histopathologic UIP pattern was present in 42 of 69 (61%) patients. Men were more likely than women to have a histopathologic UIP pattern (P = .02). Twenty patients (29%, 20 of 69) had a definite UIP pattern on CT scans. The specificity of CT UIP pattern was 96% (26 of 27; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 81%, 100%), with a negative predictive value of 53% (26 of 49). The sensitivity of CT UIP pattern was 45% (19 of 42; 95% CI: 30%, 61%), with a positive predictive value of 95% (19 of 20). The agreement between radiologists for definite UIP pattern versus not was 87% (κ = 0.67, P < .0001).
Conclusion: Definite UIP pattern on a CT scan in RA-ILD is highly specific and moderately sensitive for histopathologic UIP pattern. CT can therefore help accurately identify the UIP pattern in RA-ILD.
© RSNA, 2013
Figures



References
-
- Gabriel SE. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2001;27(2):269–281. - PubMed
-
- Lee HK, Kim DS, Yoo B, et al. . Histopathologic pattern and clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Chest 2005;127(6):2019–2027. - PubMed
-
- Yoshinouchi T, Ohtsuki Y, Fujita J, et al. . Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia pattern as pulmonary involvement of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 2005;26(2):121–125. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka N, Kim JS, Newell JD, et al. . Rheumatoid arthritis-related lung diseases: CT findings. Radiology 2004;232(1):81–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

