Chlorella 11-peptide inhibits the production of macrophage-induced adhesion molecules and reduces endothelin-1 expression and endothelial permeability
- PMID: 24129228
- PMCID: PMC3826139
- DOI: 10.3390/md11103861
Chlorella 11-peptide inhibits the production of macrophage-induced adhesion molecules and reduces endothelin-1 expression and endothelial permeability
Abstract
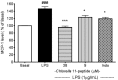
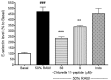
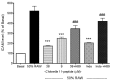
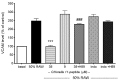
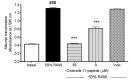
The inflammation process in large vessels involves the up-regulation of vascular adhesion molecules such as endothelial cell selectin (E-selectin), intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) which are also known as the markers of atherosclerosis. We have reported that Chlorella 11-peptide exhibited effective anti-inflammatory effects. This peptide with an amino sequence Val-Glu-Cys-Tyr-Gly-Pro-Asn-Arg-Pro-Gln-Phe was further examined for its potential in preventing atherosclerosis in this study. In particular, the roles of Chlorella 11-peptide in lowering the production of vascular adhesion molecules, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1) and expression of endothelin-1 (ET-1) from endothelia (SVEC4-10 cells) were studied. The production of E-selectin, ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and MCP-1 in SVEC4-10 cells was measured with ELISA. The mRNA expression of ET-1 was analyzed by RT-PCR and agarose gel. Results showed that Chlorella 11-peptide significantly suppressed the levels of E-selectin, ICAM, VCAM, MCP-1 as well as ET-1 gene expression. The inhibition of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 production by Chlorella 11-peptide was reversed in the presence of protein kinase A inhibitor (H89) which suggests that the cAMP pathway was involved in the inhibitory cause of the peptide. In addition, this peptide was shown to reduce the extent of increased intercellular permeability induced by combination of 50% of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW 264.7 cells medium and 50% normal SEVC cell culture medium (referred to as 50% RAW-conditioned medium). These data demonstrate that Chlorella 11-peptide is a promising biomolecule in preventing chronic inflammatory-related vascular diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neutralization of TNF by the antibody cA2 reveals differential regulation of adhesion molecule expression on TNF-activated endothelial cells.Cell Adhes Commun. 1998 Sep;5(6):491-503. doi: 10.3109/15419069809005606. Cell Adhes Commun. 1998. PMID: 9791729
-
Multiple anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic properties of red wine polyphenolic extracts: differential role of hydroxycinnamic acids, flavonols and stilbenes on endothelial inflammatory gene expression.Eur J Nutr. 2016 Mar;55(2):477-489. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-0865-6. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Eur J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 25724173
-
Leukocyte adhesion molecule and chemokine production through lipoteichoic acid recognition by toll-like receptor 2 in cultured human lymphatic endothelium.Cell Tissue Res. 2008 Aug;333(2):237-52. doi: 10.1007/s00441-008-0625-5. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Cell Tissue Res. 2008. PMID: 18523807
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Vascular Inflammation: Modulation of Endothelial Adhesion Molecules and Endothelium-Leukocyte Adhesion.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Sep 6;28(9):194. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2809194. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37796707 Review.
-
Current Nanomedicine for Targeted Vascular Disease Treatment: Trends and Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 17;23(20):12397. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012397. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory Activity of Bioactive Compounds from Microalgae and Cyanobacteria by Focusing on the Mechanisms of Action.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Aug;47(8):6193-6205. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05562-9. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32557174 Review.
-
Benefits of Preventive Administration of Chlorella sp. on Visceral Pain and Cystitis Induced by a Single Administration of Cyclophosphamide in Female Wistar Rat.J Med Food. 2016 May;19(5):450-6. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2015.0077. J Med Food. 2016. PMID: 27152976 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides from Photosynthetic Marine Organisms with Potential Application in Aquaculture.Mar Drugs. 2023 May 8;21(5):290. doi: 10.3390/md21050290. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37233484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Marine-Derived Components on Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and Gut Microbiota Diversity.Mar Drugs. 2024 Nov 20;22(11):523. doi: 10.3390/md22110523. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39590803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative Protein Sources and Novel Foods: Benefits, Food Applications and Safety Issues.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 21;15(6):1509. doi: 10.3390/nu15061509. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nasuno A., Matsubara T., Hori T., Higuchi K., Imai S., Nakagawa I., Tsuchida K., Ozaki K., Mezaki T., Tanaka T., et al. Levels of soluble E-selectin and ICAM-1 in the coronary circulation of patients with stable coronary artery disease: Association with the severity of coronary atherosclerosis. Jpn. Heart. J. 2002;43:93–101. doi: 10.1536/jhj.43.93. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

