MicroRNA profile: a promising ancillary tool for accurate renal cell tumour diagnosis
- PMID: 24129247
- PMCID: PMC3833202
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.552
MicroRNA profile: a promising ancillary tool for accurate renal cell tumour diagnosis
Abstract
Background: Renal cell tumours (RCTs) are clinically, morphologically and genetically heterogeneous. Accurate identification of renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) and its discrimination from normal tissue and benign tumours is mandatory. We, thus, aimed to define a panel of microRNAs that might aid in the diagnostic workup of RCTs.
Methods: Fresh-frozen tissues from 120 RCTs (clear-cell RCC, papillary RCC, chromophobe RCC (chRCC) and oncocytomas: 30 cases each), 10 normal renal tissues and 60 cases of ex-vivo fine-needle aspiration biopsies from RCTs (15 of each subtype validation set) were collected. Expression levels of miR-21, miR-141, miR-155, miR-183 and miR-200b were assessed by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Receiver operator characteristic curves were constructed and the areas under the curve were calculated to assess diagnostic performance. Disease-specific survival curves and a Cox regression model comprising all significant variables were computed.
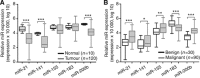
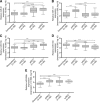
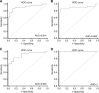
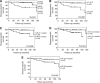
Results: Renal cell tumours displayed significantly lower expression levels of miR-21, miR-141 and miR-200b compared with that of normal tissues, and expression levels of all miRs differed significantly between malignant and benign RCTs. Expression analysis of miR-141 or miR-200b accurately distinguished RCTs from normal renal tissues, oncocytoma from RCC and chRCC from oncocytoma. The diagnostic performance was confirmed in the validation set. Interestingly, miR-21, miR-141 and miR-155 expression levels showed prognostic significance in a univariate analysis.
Conclusion: The miR-141 or miR-200b panel accurately distinguishes RCC from normal kidney and oncocytoma in tissue samples, discriminating from normal kidney and oncocytoma, whereas miR-21, miR-141 and miR-155 convey prognostic information. This approach is feasible in fine-needle aspiration biopsies and might provide an ancillary tool for routine diagnosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma using a three-gene promoter methylation panel.J Transl Med. 2017 Jun 29;15(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1248-y. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28662726 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic expression and single-nucleotide polymorphism profiling discriminates chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma.BMC Cancer. 2010 May 12;10:196. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-196. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20462447 Free PMC article.
-
Ancillary studies in fine needle aspiration of the kidney.Cancer Cytopathol. 2018 Aug;126 Suppl 8:711-723. doi: 10.1002/cncy.22029. Cancer Cytopathol. 2018. PMID: 30156770 Review.
-
Claudin-7 immunohistochemistry in renal tumors: a candidate marker for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma identified by gene expression profiling.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007 Oct;131(10):1541-6. doi: 10.5858/2007-131-1541-CIIRTA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007. PMID: 17922590
-
Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic potential of exosomal microRNAs in renal cancer.Pharmacol Rep. 2024 Apr;76(2):273-286. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00568-7. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Pharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38388810 Review.
Cited by
-
Cooperative Effect of miR-141-3p and miR-145-5p in the Regulation of Targets in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 23;11(6):e0157801. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157801. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27336447 Free PMC article.
-
SRMDAP: SimRank and Density-Based Clustering Recommender Model for miRNA-Disease Association Prediction.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Mar 21;2018:5747489. doi: 10.1155/2018/5747489. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29750163 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NHERF1 in MicroRNA Landscape Changes in Aging Mouse Kidneys.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 23;14(9):1048. doi: 10.3390/biom14091048. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334814 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression profiles predict clinical phenotypes and prognosis in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2015 May 18;5:10328. doi: 10.1038/srep10328. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25981392 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma using a three-gene promoter methylation panel.J Transl Med. 2017 Jun 29;15(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1248-y. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28662726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahams NA, MacLennan GT, Khoury JD, Ormsby AH, Tamboli P, Doglioni C, Schumacher B, Tickoo SK. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: a comparative study of histological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural features using high throughput tissue microarray. Histopathology. 2004;45 (6:593–602. - PubMed
-
- Amin MB, Tamboli P, Javidan J, Stricker H, de-Peralta Venturina M, Deshpande A, Menon M. Prognostic impact of histologic subtyping of adult renal epithelial neoplasms: an experience of 405 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26 (3:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Baldewijns MM, van Vlodrop IJ, Schouten LJ, Soetekouw PM, de Bruine AP, van Engeland M. Genetics and epigenetics of renal cell cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1785 (2:133–155. - PubMed
-
- Biosystems A.2004. Guide to Performing Relative Quantitation of Gene Expression Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR: Applied Biosystems.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

