Dysregulation in lung immunity - the protective and pathologic Th17 response in infection
- PMID: 24130019
- PMCID: PMC3947216
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201343713
Dysregulation in lung immunity - the protective and pathologic Th17 response in infection
Abstract
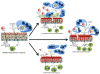
Th17 cytokines can play both protective and pathologic roles in the airways. An emerging theme in Th17 cytokine biology is that these responses can mediate tissue pathology when downstream effector cells are dysfunctional, such as neutrophils lacking functional NADPH oxidase in the case of chronic granulomatous disease, or epithelial cells lacking appropriate ion transport as in the case of cystic fibrosis. In this Mini-Review we highlight recent advances in the protective and pathologic roles of Th17 cytokines in the context of infection at the pulmonary barrier.
Keywords: Animal models; CD4 T cells; Cellular immunology; Cytokines; Lung inflammation.
© 2013 WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- McGeachy MJ, Cua DJ. Th17 cell differentiation: the long and winding road. Immunity. 2008;28:445–453. - PubMed
-
- Bordon J, Aliberti S, Fernandez-Botran R, Uriarte SM, Rane MJ, Duvvuri P, Peyrani P, Morlacchi LC, Blasi F, Ramirez JA. Understanding the roles of cytokines and neutrophil activity and neutrophil apoptosis in the protective versus deleterious inflammatory response in pneumonia. Int J Infect Dis. 2013;17:e76–83. - PubMed
-
- Ye P, Rodriguez FH, Kanaly S, Stocking KL, Schurr J, Schwarzenberger P, Oliver P, Huang W, Zhang P, Zhang J, Shellito JE, Bagby GJ, Nelson S, Charrier K, Peschon JJ, Kolls JK. Requirement of interleukin 17 receptor signaling for lung CXC chemokine and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor expression, neutrophil recruitment, and host defense. J Exp Med. 2001;194:519–527. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

