Plant purine nucleoside catabolism employs a guanosine deaminase required for the generation of xanthosine in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 24130159
- PMCID: PMC3877791
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.117184
Plant purine nucleoside catabolism employs a guanosine deaminase required for the generation of xanthosine in Arabidopsis
Abstract
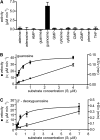
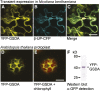
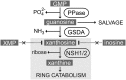
Purine nucleotide catabolism is common to most organisms and involves a guanine deaminase to convert guanine to xanthine in animals, invertebrates, and microorganisms. Using metabolomic analysis of mutants, we demonstrate that Arabidopsis thaliana uses an alternative catabolic route employing a highly specific guanosine deaminase (GSDA) not reported from any organism so far. The enzyme is ubiquitously expressed and deaminates exclusively guanosine and 2'-deoxyguanosine but no other aminated purines, pyrimidines, or pterines. GSDA belongs to the cytidine/deoxycytidylate deaminase family of proteins together with a deaminase involved in riboflavin biosynthesis, the chloroplastic tRNA adenosine deaminase Arg and a predicted tRNA-specific adenosine deaminase 2 in A. thaliana. GSDA is conserved in plants, including the moss Physcomitrella patens, but is absent in the algae and outside the plant kingdom. Our data show that xanthosine is exclusively generated through the deamination of guanosine by GSDA in A. thaliana, excluding other possible sources like the dephosphorylation of xanthosine monophosphate. Like the nucleoside hydrolases NUCLEOSIDE HYDROLASE1 (NSH1) and NSH2, GSDA is located in the cytosol, indicating that GMP catabolism to xanthine proceeds in a mostly cytosolic pathway via guanosine and xanthosine. Possible implications for the biosynthetic route of purine alkaloids (caffeine and theobromine) and ureides in other plants are discussed.
Figures



References
-
- Alonso J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Ashihara H. (2012). Xanthosine metabolism in plants: Metabolic fate of exogenously supplied C-14-labelled xanthosine and xanthine in intact mungbean seedlings. Phytochem. Lett. 5: 100–103
-
- Ashihara H., Sano H., Crozier A. (2008). Caffeine and related purine alkaloids: Biosynthesis, catabolism, function and genetic engineering. Phytochemistry 69: 841–856 - PubMed
-
- Ashihara H., Takasawa Y., Suzuki T. (1997). Metabolic fate of guanosine in higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 100: 909–916
-
- Brychkova G., Alikulov Z., Fluhr R., Sagi M. (2008). A critical role for ureides in dark and senescence-induced purine remobilization is unmasked in the Atxdh1 Arabidopsis mutant. Plant J. 54: 496–509 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

