A two-hybrid-receptor assay demonstrates heteromer formation as switch-on for plant immune receptors
- PMID: 24130196
- PMCID: PMC3850202
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.227736
A two-hybrid-receptor assay demonstrates heteromer formation as switch-on for plant immune receptors
Abstract
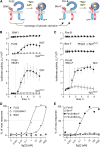
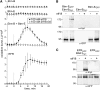
Receptor kinases sense extracellular signals and trigger intracellular signaling and physiological responses. However, how does signal binding to the extracellular domain activate the cytoplasmic kinase domain? Activation of the plant immunoreceptor Flagellin sensing2 (FLS2) by its bacterial ligand flagellin or the peptide-epitope flg22 coincides with rapid complex formation with a second receptor kinase termed brassinosteroid receptor1 associated kinase1 (BAK1). Here, we show that the receptor pair of FLS2 and BAK1 is also functional when the roles of the complex partners are reversed by swapping their cytosolic domains. This reciprocal constellation prevents interference by redundant partners that can partially substitute for BAK1 and demonstrates that formation of the heteromeric complex is the molecular switch for transmembrane signaling. A similar approach with swaps between the Elongation factor-Tu receptor and BAK1 also resulted in a functional receptor/coreceptor pair, suggesting that a "two-hybrid-receptor assay" is of more general use for studying heteromeric receptor complexes.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

