MIRD pamphlet No. 24: Guidelines for quantitative 131I SPECT in dosimetry applications
- PMID: 24130233
- PMCID: PMC3970715
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.113.122390
MIRD pamphlet No. 24: Guidelines for quantitative 131I SPECT in dosimetry applications
Abstract
The reliability of radiation dose estimates in internal radionuclide therapy is directly related to the accuracy of activity estimates obtained at each imaging time point. The recently published MIRD pamphlet no. 23 provided a general overview of quantitative SPECT imaging for dosimetry. The present document is the first in a series of isotope-specific guidelines that will follow MIRD 23 and focuses on one of the most commonly used therapeutic radionuclides, (131)I. The purpose of this document is to provide guidance on the development of protocols for quantitative (131)I SPECT in radionuclide therapy applications that require regional (normal organs, lesions) and 3-dimensional dosimetry.
Keywords: 131I; MIRD; SPECT/CT, dosimetry; quantitative SPECT.
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

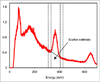

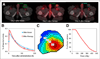
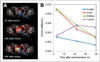
References
-
- Zeintl J, Vija AH, Yahil A, Hornegger J, Kuwert T. Quantitative accuracy of clinical99mTc SPECT/CT using ordered-subset expectation maximization with 3-dimensional resolution recovery, attenuation, and scatter correction. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:921–928. - PubMed
-
- Ljungberg M, Strand SE. A Monte Carlo program for the simulation of scintillation camera characteristics. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1989;29:257–272. - PubMed
-
- Bolster A. Quality Control of Gamma Camera Systems. York, United Kingdom: Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine; 2003. p. 86.
-
- Buckley SE, Saran FH, Gaze MN, et al. Dosimetry for fractionated 131I-mIBG therapies in patients with primary resistant high-risk neuroblastoma: preliminary results. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2007;22:105–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
