Ideal cardiovascular health and the prevalence and progression of coronary artery calcification in adults with and without type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 24130360
- PMCID: PMC3898750
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-0997
Ideal cardiovascular health and the prevalence and progression of coronary artery calcification in adults with and without type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: In 2010, the American Heart Association defined seven metrics (smoking, BMI, physical activity, diet, total cholesterol, blood pressure, and fasting plasma glucose) for ideal cardiovascular health (ICH). Subsequent studies have shown that the prevalence of achieving these metrics is very low in the general population. Adults with type 1 diabetes are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), but no studies to date have been published on the prevalence of ICH in this population.
Research design and methods: Data for this analysis were collected as part of the prospective Coronary Artery Calcification in Type 1 Diabetes study. This analysis involved 546 subjects with type 1 diabetes and 631 subjects without diabetes who had complete information for calculating the ICH metrics.
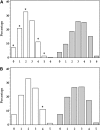
Results: Overall, the prevalence of ICH was low in this population, with none meeting the ideal criteria for all seven metrics. The prevalence of ideal physical activity (10.0%) and diet (1.1%) were particularly low. ICH was significantly associated with both decreased prevalence (odds ratio [OR] 0.70; 95% CI 0.62-0.80) and progression (OR 0.77; 95% CI 0.66-0.90) of coronary artery calcification (CAC).
Conclusions: ICH is significantly associated with decreased prevalence and progression of CAC; however, prevalence of ICH metrics was low in adults both with and without type 1 diabetes. Efforts to increase the prevalence of ICH could have a significant impact on reducing the burden of CVD.
Figures
References
-
- Forlenza GP, Rewers M. The epidemic of type 1 diabetes: what is it telling us? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2011;18:248–251 - PubMed
-
- Laing SP, Swerdlow AJ, Slater SD, et al. Mortality from heart disease in a cohort of 23,000 patients with insulin-treated diabetes. Diabetologia 2003;46:760–765 - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Nathan DM, Abraham K, et al. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Working Group on Cardiovascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute-National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Working Group on Cardiovascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2005;111:3489–3493 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

