Structure of a bimodular botulinum neurotoxin complex provides insights into its oral toxicity
- PMID: 24130488
- PMCID: PMC3795040
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003690
Structure of a bimodular botulinum neurotoxin complex provides insights into its oral toxicity
Abstract
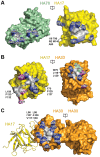
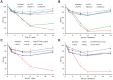
Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) are produced by Clostridium botulinum and cause the fatal disease botulism, a flaccid paralysis of the muscle. BoNTs are released together with several auxiliary proteins as progenitor toxin complexes (PTCs) to become highly potent oral poisons. Here, we report the structure of a ∼760 kDa 14-subunit large PTC of serotype A (L-PTC/A) and reveal insight into its absorption mechanism. Using a combination of X-ray crystallography, electron microscopy, and functional studies, we found that L-PTC/A consists of two structurally and functionally independent sub-complexes. A hetero-dimeric 290 kDa complex protects BoNT, while a hetero-dodecameric 470 kDa complex facilitates its absorption in the harsh environment of the gastrointestinal tract. BoNT absorption is mediated by nine glycan-binding sites on the dodecameric sub-complex that forms multivalent interactions with carbohydrate receptors on intestinal epithelial cells. We identified monosaccharides that blocked oral BoNT intoxication in mice, which suggests a new strategy for the development of preventive countermeasures for BoNTs based on carbohydrate receptor mimicry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


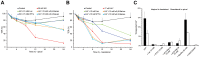
References
-
- Arnon SS, Schechter R, Inglesby TV, Henderson DA, Bartlett JG, et al. (2001) Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: medical and public health management. JAMA 285: 1059–1070. - PubMed
-
- Bigalke H (2013) Botulinum toxin: application, safety, and limitations. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 364: 307–317. - PubMed
-
- Collins MD, East AK (1998) Phylogeny and taxonomy of the food-borne pathogen Clostridium botulinum and its neurotoxins. J Appl Microbiol 84: 5–17. - PubMed
-
- Cheng LW, Onisko B, Johnson EA, Reader JR, Griffey SM, et al. (2008) Effects of purification on the bioavailability of botulinum neurotoxin type A. Toxicology 249: 123–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1S10RR23057/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103403/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 8 P41 GM103403-10/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR015301/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR001209/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR001209/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AI091823/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI091823/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023057/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5P41RR015301-10/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI065359/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

