Dopamine signaling in reward-related behaviors
- PMID: 24130517
- PMCID: PMC3795306
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00152
Dopamine signaling in reward-related behaviors
Abstract
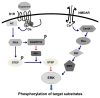
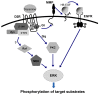
Dopamine (DA) regulates emotional and motivational behavior through the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway. Changes in DA mesolimbic neurotransmission have been found to modify behavioral responses to various environmental stimuli associated with reward behaviors. Psychostimulants, drugs of abuse, and natural reward such as food can cause substantial synaptic modifications to the mesolimbic DA system. Recent studies using optogenetics and DREADDs, together with neuron-specific or circuit-specific genetic manipulations have improved our understanding of DA signaling in the reward circuit, and provided a means to identify the neural substrates of complex behaviors such as drug addiction and eating disorders. This review focuses on the role of the DA system in drug addiction and food motivation, with an overview of the role of D1 and D2 receptors in the control of reward-associated behaviors.
Keywords: dopamine; dopamine receptor; drug addiction; food reward; reward circuit.
Figures
References
-
- Baker D. A., Khroyan T. V., O’Dell L. E., Fuchs R. A., Neisewander J. L. (1996). Differential effects of intra-accumbenssulpiride on cocaine-induced locomotion and conditioned place preference. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 279 392–401 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

