Targeting fungal genes by diced siRNAs: a rapid tool to decipher gene function in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 24130711
- PMCID: PMC3794931
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075443
Targeting fungal genes by diced siRNAs: a rapid tool to decipher gene function in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
Background: Gene silencing triggered by chemically synthesized small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) has become a powerful tool for deciphering gene function in many eukaryotes. However, prediction and validation of a single siRNA duplex specific to a target gene is often ineffective. RNA interference (RNAi) with synthetic siRNA suffers from lower silencing efficacy, off-target effects and is cost-intensive, especially for functional genomic studies. With the explosion of fungal genomic information, there is an increasing need to analyze gene function in a rapid manner. Therefore, studies were performed in order to investigate the efficacy of gene silencing induced by RNase III-diced-siRNAs (d-siRNA) in model filamentous fungus, Aspergillus nidulans.
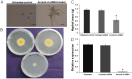
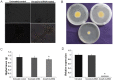
Methodology/principal findings: Stable expression of heterologous reporter gene in A. nidulans eases the examination of a new RNAi-induction route. Hence, we have optimized Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation (AMT) of A. nidulans for stable expression of sGFP gene. This study demonstrates that the reporter GFP gene stably introduced into A. nidulans can be effectively silenced by treatment of GFP-d-siRNAs. We have shown the down-regulation of two endogenous genes, AnrasA and AnrasB of A. nidulans by d-siRNAs. We have also elucidated the function of an uncharacterized Ras homolog, rasB gene, which was found to be involved in hyphal growth and development. Further, silencing potency of d-siRNA was higher as compared to synthetic siRNA duplex, targeting AnrasA. Silencing was shown to be sequence-specific, since expression profiles of other closely related Ras family genes in d-siRNA treated AnrasA and AnrasB silenced lines exhibited no change in gene expression.
Conclusions/significance: We have developed and applied a fast, specific and efficient gene silencing approach for elucidating gene function in A. nidulans using d-siRNAs. We have also optimized an efficient AMT in A. nidulans, which is useful for stable integration of transgenes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of sidB gene by use of RNA interference in Aspergillus nidulans.Iran Biomed J. 2014;18(1):55-9. doi: 10.6091/ibj.1217.2013. Iran Biomed J. 2014. PMID: 24375164 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting polyamines of Aspergillus nidulans by siRNA specific to fungal ornithine decarboxylase gene.Med Mycol. 2007 May;45(3):211-20. doi: 10.1080/13693780601158779. Med Mycol. 2007. PMID: 17464842
-
RNA silencing gene truncation in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans.Eukaryot Cell. 2008 Feb;7(2):339-49. doi: 10.1128/EC.00355-07. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Eukaryot Cell. 2008. PMID: 18065653 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol catabolism in Aspergillus nidulans: a model system for studying gene regulation.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;69:149-204. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)69047-0. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11550794 Review.
-
RNA interference-based gene silencing in mice: the development of a novel therapeutical strategy.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(26):3405-19. doi: 10.2174/138161205774370834. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. PMID: 16250844 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-mediated RNAi silences midgut-expressed genes in congeneric lepidopteran insects in nature.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Nov 13;17(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1149-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 29132300 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Silencing of DNA Repair Genes Improves Targeted Gene Integration in the Filamentous Fungus Trichoderma reesei.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Jul 17;83(15):e00535-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00535-17. Print 2017 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28550064 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol Biosynthesis and Azole Tolerance Is Governed by the Opposing Actions of SrbA and the CCAAT Binding Complex.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Jul 20;12(7):e1005775. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005775. eCollection 2016 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27438727 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestration of Morphogenesis in Filamentous Fungi: Conserved Roles for Ras Signaling Networks.Fungal Biol Rev. 2015 Jun 1;29(2):54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.fbr.2015.04.003. Fungal Biol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26257821 Free PMC article.
-
Agrobacterium tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation of NHEJ Mutant Aspergillus nidulans Conidia: An Efficient Tool for Targeted Gene Recombination Using Selectable Nutritional Markers.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Nov 12;7(11):961. doi: 10.3390/jof7110961. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829246 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, et al. (1998) Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature 391: 806–811. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC (1999) A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 286: 950–952. - PubMed
-
- Devi GR (2006) siRNA-based approaches in cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 13: 819–829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

