Chemosignals of stress influence social judgments
- PMID: 24130845
- PMCID: PMC3793963
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077144
Chemosignals of stress influence social judgments
Abstract
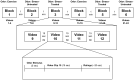
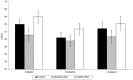
Human body odors have important communicative functions regarding genetic identity, immune fitness and general health, but an expanding body of research suggests they can also communicate information about an individual's emotional state. In the current study, we tested whether axillary odors obtained from women experiencing psychosocial stress could negatively influence personality judgments of warmth and competence made about other women depicted in video scenarios. 44 female donors provided three types of sweat samples: untreated exercise sweat, untreated stress sweat and treated stress sweat. After a 'washout' period, a commercial unscented anti-perspirant product was applied to the left axilla only to evaluate whether 'blocking' the stress signal would improve the social evaluations. A separate group of male and female evaluators (n = 120) rated the women in the videos while smelling one of the three types of sweat samples. Women in the video scenes were rated as being more stressed by both men and women when smelling the untreated vs. treated stress sweat. For men only, the women in the videos were rated as less confident, trustworthy and competent when smelling both the untreated stress and exercise sweat in contrast to the treated stress sweat. Women's social judgments were unaffected by sniffing the pads. The results have implications for influencing multiple types of professional and personal social interactions and impression management and extend our understanding of the social communicative function of body odors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Jacob S, McClintock MK, Zelano B, Ober C (2002) Paternally inherited HLA alleles are associated with women's choice of male odor. Nature Genetics 30: 175–179. - PubMed
-
- McClintock MK, Bullivant S, Jacob S, Spencer N, Zelano B, et al. (2005) Human body scents: Conscious perceptions and biological effects. Chem Senses 30: I135–i137. - PubMed
-
- Lundstrom JN, Boyle JA, Zatorre RJ, Jones-Gotman M (2008) Functional neuronal processing of body odors differs from that of similar common odors. Cereb Cortex 18: 1466–1474. - PubMed
-
- Sobel N, Prabhakaran V, Hartley CA, Desmond JE, Glover GH, et al. (1999) Blind smell: brain activation induced by an undetected air-borne chemical. Brain 122: 209–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

