Mapping of zebrafish research: a global outlook
- PMID: 24131434
- PMCID: PMC3842892
- DOI: 10.1089/zeb.2012.0854
Mapping of zebrafish research: a global outlook
Abstract
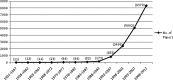
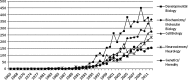
On the basis of analysis of 17,151 records on zebrafish identified from Zebrafish Information Network: the zebrafish model organism database and Web of Science, the research performance on this model organism has been evaluated. The earliest research work on zebrafish as reflected in the databases goes back to 1951. After a rather slow growth till the 1980s, research on zebrafish gained momentum in the 1990s. Analysis shows a rapid and consistent increase in the publication output with 226 publications in the year 1996, to 1929 publications in the year 2012. The prominent areas of zebrafish research, journals, and leading authors as reflected from the research output have been identified. USA is the most productive country with 8196 articles. The most frequently used keywords were also determined to gain insights about the research trends and some of the commonly used keywords other than zebrafish and Danio rerio are development, retina, and gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sri Lanka in global medical research: a scientific analysis of the Sri Lankan research output during 2000-2009.BMC Res Notes. 2012 Feb 24;5:121. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-121. BMC Res Notes. 2012. PMID: 22364509 Free PMC article.
-
Half a century of computer methods and programs in biomedicine: A bibliometric analysis from 1970 to 2017.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Jan;183:105075. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105075. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 31526946 Review.
-
Zebrafish in Brazilian Science: Scientific Production, Impact, and Collaboration.Zebrafish. 2016 Jun;13(3):217-25. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2015.1183. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Zebrafish. 2016. PMID: 27045850 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing contribution of China in modern biomedical research. Statistical data from ISI Web of Knowledge.Med Sci Monit. 2009 Dec;15(12):SR15-21. Med Sci Monit. 2009. PMID: 19946247
-
Scientometric evaluation of the global research in spine: an update on the pioneering study by Wei et al.Eur Spine J. 2018 Mar;27(3):524-529. doi: 10.1007/s00586-017-5411-1. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Eur Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29196944 Review.
Cited by
-
Zebrafish as a Useful Model System for Human Liver Disease.Cells. 2023 Sep 11;12(18):2246. doi: 10.3390/cells12182246. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37759472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioural effects of the common brain-infecting parasite Pseudoloma neurophilia in laboratory zebrafish (Danio rerio).Sci Rep. 2020 May 15;10(1):8083. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64948-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32415102 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of a Zebrafish Health Program in a Research Facility: A 4-Year Retrospective Study.Zebrafish. 2016 Jul;13 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S115-26. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2015.1230. Epub 2016 May 17. Zebrafish. 2016. PMID: 27186875 Free PMC article.
-
Internal Temperatures of Packaging for Overnight Cross-country Shipping of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio).Comp Med. 2022 Jun 1;72(3):195-203. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-22-000053. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Comp Med. 2022. PMID: 35676071 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Toxicity and Therapeutic Potential of A. dahurica and A. pubescens in Zebrafish Larvae: Insights into Anxiety Treatment Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 22;26(7):2884. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072884. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubinstein AL. Zebrafish: From disease modeling to drug discovery. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2003;6:218–223. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty C. Hsu CH. Wen ZH. Lin CS. Agoramoorthy G. Zebrafish: a complete animal model for in vivo drug discovery and development. Curr Drug Metab. 2009;10:116–124. - PubMed
-
- Lieschke GJ. Currie PD. Animal models of human disease: zebrafish swim into view. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:353–367. - PubMed
-
- Dooley K. Zon LI. Zebrafish: a model system for the study of human disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2000;10:252–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources