Expression profile of host restriction factors in HIV-1 elite controllers
- PMID: 24131498
- PMCID: PMC3827935
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-106
Expression profile of host restriction factors in HIV-1 elite controllers
Abstract
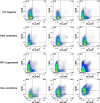
Background: Several host-encoded antiviral factors suppress HIV-1 replication in a cell-autonomous fashion in vitro. The relevance of these defenses to the control of HIV-1 in vivo remains to be elucidated. We hypothesized that cellular restriction of HIV-1 replication plays a significant role in the observed suppression of HIV-1 in "elite controllers", individuals who maintain undetectable levels of viremia in the absence of antiretroviral therapy (ART). We comprehensively compared the expression levels of 34 host restriction factors and cellular activation levels in CD4+ T cells and sorted T cell subsets between elite controllers, HIV-1-infected (untreated) non-controllers, ART-suppressed, and uninfected individuals.
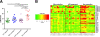
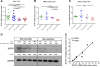
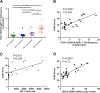
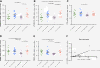
Results: Expression of schlafen 11, a codon usage-based inhibitor of HIV-1 protein synthesis, was significantly elevated in CD4+ T cells from elite controllers as compared to both non-controllers (p = 0.048) and ART-suppressed individuals (p = 0.024), with this effect most apparent in central memory CD4+ T cells. Schlafen 11 expression levels were comparable between controllers and uninfected individuals. Cumulative restriction factor expression was positively correlated with CD4+ T cell activation (r² = 0.597, p < 0.0001), viral load (r² = 0.34, p = 0.015), and expression of ISG15 (r² = 0.73, p < 0.0001), a marker of interferon exposure. APOBEC3C, APOBEC3D, CTR9, TRIM26, and TRIM32 were elevated in elite controllers with respect to ART-suppressed individuals, while levels were comparable to uninfected individuals and non-controllers.
Conclusions: Host restriction factor expression typically scales with cellular activation levels. However, the elevated mRNA and protein expression of schlafen 11, despite low activation and viral load, violates the global pattern and may be a signature characteristic of HIV-1 elite control.
Figures
References
-
- Blankson JN, Bailey JR, Thayil S, Yang HC, Lassen K, Lai J, Gandhi SK, Siliciano JD, Williams TM, Siliciano RF. Isolation and characterization of replication-competent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from a subset of elite suppressors. J Virol. 2007;81:2508. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02165-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI93179/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI096109/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1K01DA024654/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI087145/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI067039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM101982/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH62246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI090935/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI069994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI096109/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

