Dispelling myths about rare disease registry system development
- PMID: 24131574
- PMCID: PMC4015362
- DOI: 10.1186/1751-0473-8-21
Dispelling myths about rare disease registry system development
Erratum in
-
Correction: Dispelling myths about rare disease registry system development.Source Code Biol Med. 2014 Jan 31;9(1):4. doi: 10.1186/1751-0473-9-4. Source Code Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24484969 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
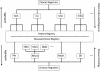
Rare disease registries (RDRs) are an essential tool to improve knowledge and monitor interventions for rare diseases. If designed appropriately, patient and disease related information captured within them can become the cornerstone for effective diagnosis and new therapies. Surprisingly however, registries possess a diverse range of functionality, operate in different, often-times incompatible, software environments and serve various, and sometimes incongruous, purposes. Given the ambitious goals of the International Rare Diseases Research Consortium (IRDiRC) by 2020 and beyond, RDRs must be designed with the agility to evolve and efficiently interoperate in an ever changing rare disease landscape, as well as to cater for rapid changes in Information Communication Technologies. In this paper, we contend that RDR requirements will also evolve in response to a number of factors such as changing disease definitions and diagnostic criteria, the requirement to integrate patient/disease information from advances in either biotechnology and/or phenotypying approaches, as well as the need to adapt dynamically to security and privacy concerns. We dispel a number of myths in RDR development, outline key criteria for robust and sustainable RDR implementation and introduce the concept of a RDR Checklist to guide future RDR development.
Figures
References
-
- Evans SM. et al.Development of clinical-quality registries in Australia: the way forward. Med J Aust. 2011;8(7):360–363. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources