The epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 24132149
- PMCID: PMC3821633
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms141020597
The epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in cardiovascular disease
Abstract
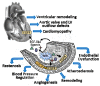
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family and its ligands serve as a switchboard for the regulation of multiple cellular processes. While it is clear that EGFR activity is essential for normal cardiac development, its function in the vasculature and its role in cardiovascular disease are only beginning to be elucidated. In the blood vessel, endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells are both a source and a target of EGF-like ligands. Activation of EGFR has been implicated in blood pressure regulation, endothelial dysfunction, neointimal hyperplasia, atherogenesis, and cardiac remodeling. Furthermore, increased circulating EGF-like ligands may mediate accelerated vascular disease associated with chronic inflammation. Although EGFR inhibitors are currently being used clinically for the treatment of cancer, additional studies are necessary to determine whether abrogation of EGFR signaling is a potential strategy for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Figures

References
-
- Holbro T., Hynes N.E. ErbB receptors: Directing key signaling networks throughout life. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004;44:195–217. - PubMed
-
- Hackel P.O., Zwick E., Prenzel N., Ullrich A. Epidermal growth factor receptors: Critical mediators of multiple receptor pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1999;11:184–189. - PubMed
-
- Wetzker R., Bohmer F.D. Transactivation joins multiple tracks to the ERK/MAPK cascade. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:651–657. - PubMed
-
- Prenzel N., Zwick E., Daub H., Leserer M., Abraham R., Wallasch C., Ullrich A. EGF receptor transactivation by G-protein-coupled receptors requires metalloproteinase cleavage of proHB-EGF. Nature. 1999;402:884–888. - PubMed
-
- Prenzel N., Fischer O.M., Streit S., Hart S., Ullrich A. The epidermal growth factor receptor family as a central element for cellular signal transduction and diversification. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2001;8:11–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

