Carboxy terminus and pore-forming domain properties specific to Cx37 are necessary for Cx37-mediated suppression of insulinoma cell proliferation
- PMID: 24133065
- PMCID: PMC3882364
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00159.2013
Carboxy terminus and pore-forming domain properties specific to Cx37 are necessary for Cx37-mediated suppression of insulinoma cell proliferation
Abstract
Connexin 37 (Cx37) suppresses cell proliferation when expressed in rat insulinoma (Rin) cells, an effect also manifest in vivo during vascular development and in response to tissue injury. Mutant forms of Cx37 with nonfunctional channels but normally localized, wild-type carboxy termini are not growth suppressive. Here we determined whether the carboxy-terminal (CT) domain is required for Cx37-mediated growth suppression and whether the Cx37 pore-forming domain can be replaced with the Cx43 pore-forming domain and still retain growth-suppressive properties. We show that despite forming functional gap junction channels and hemichannels, Cx37 with residues subsequent to 273 replaced with a V5-epitope tag (Cx37-273tr*V5) had no effect on the proliferation of Rin cells, did not facilitate G1-cell cycle arrest with serum deprivation, and did not prolong cell cycle time comparably to the wild-type protein. The chimera Cx43*CT37, comprising the pore-forming domain of Cx43 and CT of Cx37, also did not suppress proliferation, despite forming functional gap junctions with a permselective profile similar to wild-type Cx37. Differences in channel behavior of both Cx37-273tr*V5 and Cx43*CT37 relative to their wild-type counterparts and failure of the Cx37-CT to interact as the Cx43-CT does with the Cx43 cytoplasmic loop suggest that the Cx37-CT and pore-forming domains are both essential to growth suppression by Cx37.
Keywords: connexin; endothelium; gap junction channel; growth suppression; protein interactome.
Figures



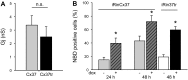

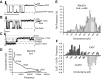

Similar articles
-
A functional channel is necessary for growth suppression by Cx37.J Cell Sci. 2011 Jul 15;124(Pt 14):2448-56. doi: 10.1242/jcs.081695. Epub 2011 Jun 21. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21693589 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular loop cysteine mutant of cx37 fails to suppress proliferation of rat insulinoma cells.J Membr Biol. 2012 Jul;245(7):369-80. doi: 10.1007/s00232-012-9459-x. Epub 2012 Jul 15. J Membr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22797939 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants and proliferative consequences of connexin 37 hemichannel function in insulinoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 31;289(44):30379-30386. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.583054. Epub 2014 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25217644 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging issues of connexin channels: biophysics fills the gap.Q Rev Biophys. 2001 Aug;34(3):325-472. doi: 10.1017/s0033583501003705. Q Rev Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11838236 Review.
-
Mutations in cardiovascular connexin genes.Biol Cell. 2014 Sep;106(9):269-93. doi: 10.1111/boc.201400038. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24966059 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Cx37 channel and growth-suppressive properties by phosphorylation.J Cell Sci. 2017 Oct 1;130(19):3308-3321. doi: 10.1242/jcs.202572. Epub 2017 Aug 17. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28818996 Free PMC article.
-
Serine 319 phosphorylation is necessary and sufficient to induce a Cx37 conformation that leads to arrested cell cycling.J Cell Sci. 2020 Jun 18;133(12):jcs240721. doi: 10.1242/jcs.240721. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32350069 Free PMC article.
-
High bone mass in mice lacking Cx37 because of defective osteoclast differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 21;289(12):8508-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.529735. Epub 2014 Feb 7. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24509854 Free PMC article.
-
Cx43 Channel Gating and Permeation: Multiple Phosphorylation-Dependent Roles of the Carboxyl Terminus.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 4;19(6):1659. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061659. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29867029 Free PMC article.
-
An Analysis Regarding the Association Between Connexins and Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Tumor Microenvironment.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Apr 15;15:2461-2476. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S361362. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35449599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcolea S, Jarry-Guichard T, de Bakker J, Gonzalez D, Lamers W, Coppen S, Barrio L, Jongsma H, Gros D, Van Rijen H. Replacement of connexin40 by connexin45 in the mouse: impact on cardiac electrical conduction. Circ Res 94: 100–109, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Angelillo-Scherrer A, Fontana P, Burnier L, Roth I, Sugamele R, Brisset A, Morel S, Nolli S, Sutter E, Chassot A, Capron C, Borgel D, Saller F, Chanson M, Kwak BR. Connexin 37 limits thrombus propensity by downregulating platelet reactivity. Circulation 124: 930–939, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Anumonwo JM, Taffet SM, Gu H, Chanson M, Moreno AP, Delmar M. The carboxyl terminal domain regulates the unitary conductance and voltage dependence of connexin40 gap junction channels. Circ Res 88: 666–673, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Boerma M, Forsberg L, Van Zeijl L, Morgenstern R, De Faire U, Lemne C, Erlinge D, Thulin T, Hong Y, Cotgreave IA. A genetic polymorphism in connexin 37 as a prognostic marker for atherosclerotic plaque development. J Intern Med 246: 211–218, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

