Outcomes of total knee arthroplasty following high tibial osteotomy
- PMID: 24133306
- PMCID: PMC3796919
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5413.118202
Outcomes of total knee arthroplasty following high tibial osteotomy
Abstract
Background: Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) following high tibial osteotomy (HTO) is a technically demanding procedure with varying results. The purpose of our study was to analyze the clinicoradiological results of TKA following HTO and to identify the factors that may influence the final outcome.
Materials and methods: 55 patients (58 knees) who had undergone a previous HTO were treated with a TKA from 1991 to 2009. There were 34 female and 21 male patients. The average age was 61.9 years (range 52-82 years) and the average weight was 79.5 kg (range 54-106 kg), with an average body mass index of 29.6 (range 21.8-34.6) at the time of TKA. The knee society scores (KSSs) and knee society functional scores were evaluated for every patient pre and postoperatively and the results evaluated.
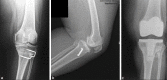
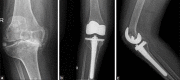
Results: The mean period of followup was 11.2 years (range 3-18 years) and the patients were followed up every year. The average KSS score at final followup improved from 38.5 (range 0-80 points) preoperatively to 88.5 postoperatively (range 35-95 points) (P < 0.05). The mean femorotibial angle corrected from 6.8 degrees (range 5-12°) varus preoperatively to a valgus of 4.4 (2-8°) degrees postoperatively. The average joint line height improved to an average of 9.6 mm (range 4.4-22 mm) (P < 0.01) at the last followup. The average Insall Salvatti Ratio also improved (average 1.11 preoperative - 1.21 average postoperative) (P < 0.05). The average range of motion improved to 108° (range 85°-125°) from 76° preoperative (range 55°-100°) (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Although TKA postHTO is a demanding surgery however, with newer component designs, results are comparable to primary TKA. Technical difficulties in exposure can sometimes lead to component malpositioning, which can affect the final outcome. Inadequate soft tissue balancing and limb malalignment should always be kept in mind. Regular followup to look for evidences of loosening is advised in such patients].
Keywords: Femorotibial angle; high tibial osteotomy; total knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computer Navigation Technique for Simultaneous Total Knee Arthroplasty and Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in Patients with Large Tibial Varus Deformity.Surg Technol Int. 2020 Nov 28;37:265-274. Surg Technol Int. 2020. PMID: 33238026
-
Long-term results of total knee arthroplasty following high tibial osteotomy according to Wagner.Int Orthop. 2012 Apr;36(4):761-4. doi: 10.1007/s00264-011-1373-9. Epub 2011 Oct 9. Int Orthop. 2012. PMID: 21983941 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Tibial Component Coronal Alignment During Total Knee Arthroplasty with the Use of a Double-Check Technique.Orthop Surg. 2019 Dec;11(6):1013-1019. doi: 10.1111/os.12570. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Orthop Surg. 2019. PMID: 31755233 Free PMC article.
-
Total knee arthroplasty following high tibial osteotomy - a radiological evaluation.Maedica (Bucur). 2011 Jan;6(1):23-7. Maedica (Bucur). 2011. PMID: 21977186 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of total knee arthroplasty following high tibial osteotomy versus primary total knee arthroplasty.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020 Apr;140(4):527-535. doi: 10.1007/s00402-020-03333-6. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020. PMID: 32002662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Total knee arthroplasty conversion after a failed lateral closing wedge high tibial osteotomy with knee hyperextension and secondary ankle degeneration: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jul;96(29):e7473. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007473. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28723758 Free PMC article.
-
Total knee arthroplasty after failed high tibial osteotomy: a systematic review of open versus closed wedge osteotomy.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016 Aug;24(8):2567-77. doi: 10.1007/s00167-015-3807-1. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016. PMID: 26423055
-
Primary cementless total knee arthroplasty with or without stem extension: a matched comparative study of ninety eight standard stems versus ninety eight long stems after more than ten years of follow-up.Int Orthop. 2019 Aug;43(8):1849-1857. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4191-5. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Int Orthop. 2019. PMID: 30284003
References
-
- Coventry MB. Osteotomy of the upper portion of the tibia for degenerative arthritis of the knee: A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg. 1965;47:984–90. - PubMed
-
- Coventry MB, Iilstrup DM, Wallrichs SL. Proximal tibial osteotomy: A critical long term study of 87 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75:196–201. - PubMed
-
- Haslam P, Armstrong M, Geutjens G, Wilton TJ. Total knee arthroplasty after failed high tibial osteotomy: Long term follow up of matched groups. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:245–50. - PubMed
-
- Mont MA, Alexander N, Krackow KA, Hungerford DS. Total knee arthroplasty after failed high tibial osteotomy. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994;25:515–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
