Acute arterial thrombosis associated with inadvertent high dose of tranexamic acid
- PMID: 24133333
- PMCID: PMC3796904
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-5229.118443
Acute arterial thrombosis associated with inadvertent high dose of tranexamic acid
Abstract
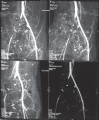
Tranexamic acid (TA) act as anti-fibrinolytic agent and is widely used to limit bleeding in clinical practice. Tranexemic acid bind with plasminogen and prevent its conversion to plasmin, which limits the fibrinolytic pathway, so there is a theoretical risk of increasing thrombosis with high or prolonged therapy with TA. We encountered a case of acute arterial thrombosis following inadvertent administration of high dose of TA. A 27-years-old male with no other co-morbidity was ordered intravenous 1 gm TA to control excessive bleeding from previous bladder injury, but by mistake, he received 10 gm of TA. The patient developed signs and symptoms of acute ischemia in the right lower limb, which was diagnosed as acute iliac arterial thrombosis by computed tomography (CT) angiography. The patient was managed with systemic heparinization, fasciotomy for impending gangrene and other supportive care following which he recovered fully within a few days. Caution should be exercised for all prophylactic use, especially with high dosage or prolonged therapy with TA.
Keywords: Arterial thrombosis; hemorrhage control; thrombo-embolism; tranexamic acid.
Figures
References
-
- CRASH-2 trial collaborators. Effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events, and blood transfusion in trauma patients with significant haemorrhage: A randomised, placebo controlled trial. The Lancet. 2010;376:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Ramstrom G, Blomback M, Egberg N, Johnsson H, Ljungberg B, Schulman S. Oral surgery in patients with hereditary bleeding disorders. A survey of treatment in the Stockholm area (1974-1985) Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989;18:320–2. - PubMed
-
- Endo Y, Nishimura S, Miura A. Deep-vein thrombosis induced by tranexamic acid in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura [letter] JAMA. 1988;259:3561–2. - PubMed
-
- Woo KS, Tse LK, Woo JL. Massive pulmonary thromboembolism after tranexamic acid antifibrinolytic therapy. Br J Clin Pract. 1989;43:465–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources