Expression of semaphorin 3A and neuropilin 1 in asthma
- PMID: 24133346
- PMCID: PMC3792596
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.10.1435
Expression of semaphorin 3A and neuropilin 1 in asthma
Abstract
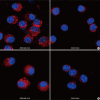
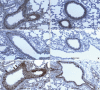
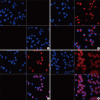
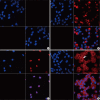
Neuropilin 1 (NP1) is a part of essential receptor complexes mediating both semaphorin3A (SEMA3A) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) which is one of important mediators involved in the pathogenesis of asthma. Therefore, it is possible that SEMA3A plays a role in the pathogenesis of asthma through attenuation of VEGF-mediated effects. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate expression levels of SEMA3A and NP1 using induced sputum of asthmatics and a murine model of asthma. Firstly, SEMA3A and NP1 expressions in induced sputum of asthmatics and SEMA3A and NP1 expression on bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells and lung homogenates of asthmatic mice were determined. Then we evaluated the immunolocalization of VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR1), VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2), and NP1 expressions on asthmatic mice lung tissue and their subcellular distributions using fibroblast and BEAS2B cell lines. Sputum SEMA3A and NP1 expressions were significantly higher in asthmatics than controls. Similarly, SEMA3A and NP1 expressions on BAL cells and lung homogenates were significantly elevated in asthmatic mice compared to control mice. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and NP1 expressions were also uniformly increased in asthmatic mice. Our observations suggest that SEMA3A and NP1 may play important roles in the pathogenesis of asthma.
Keywords: Asthma; Neuropilin; Semaphorin-3A (SEMA3A); Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no proprietary, commercial, or financial interests that could be construed to have inappropriately influenced this study.
Figures
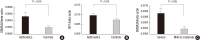
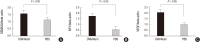
Similar articles
-
Gene expression of neuropilin-1 and its receptors, VEGF/Semaphorin 3a, in normal and cancer cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2011 Jan;59(1):39-47. doi: 10.1007/s12013-010-9109-9. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2011. PMID: 20711684
-
Semaphorin-3A and semaphorin-3F work together to repel endothelial cells and to inhibit their survival by induction of apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 7;282(36):26294-305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609711200. Epub 2007 Jun 14. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17569671
-
Human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation from asthmatics is negatively regulated by semaphorin3A.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80238-80251. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12884. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27791986 Free PMC article.
-
Competing autocrine pathways involving alternative neuropilin-1 ligands regulate chemotaxis of carcinoma cells.Cancer Res. 2003 Sep 1;63(17):5230-3. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14500350
-
The role of semaphorin 3A in the pathogenesis and progression of Alzheimer's disease and other aging-related diseases: A comprehensive review.Pharmacol Res. 2025 May;215:107732. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107732. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Pharmacol Res. 2025. PMID: 40222695 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis identifies the effects of Sema3A/NRP1 signaling in oligodendrocytes after spinal cord injury in rats.PeerJ. 2022 Aug 16;10:e13856. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13856. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35990904 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin-3A: a promising therapeutic tool in allergic rhinitis.Immunol Res. 2022 Apr;70(2):135-142. doi: 10.1007/s12026-022-09264-1. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35031951 Review.
-
[The involvement of neuropilin-1 in primary immune thrombocytopenia].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Feb 14;42(2):146-150. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2021.02.010. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33858046 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Semaphorin 3A: A Potential Target for Low Back Pain.Front Aging Neurosci. 2015 Nov 26;7:216. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00216. eCollection 2015. Front Aging Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26635602 Free PMC article.
-
Serum neuropilin-1 level may predict airway remodeling based on age and smoking status in asthma.Asia Pac Allergy. 2025 Jun;15(2):63-66. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.0000000000000192. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Asia Pac Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40718119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holgate ST. Airway inflammation and remodeling in asthma: current concepts. Mol Biotechnol. 2002;22:179–189. - PubMed
-
- Gerber HP, Dixit V, Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces expression of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and A1 in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13313–13316. - PubMed
-
- Clauss M. Molecular biology of the VEGF and the VEGF receptor family. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000;26:561–569. - PubMed
-
- Hoshino M, Takahashi M, Aoike N. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and angiogenin immunoreactivity in asthmatic airways and its relationship to angiogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:295–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

