Advanced ultrasonography technologies to assess the effects of radiofrequency ablation on hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 24133386
- PMCID: PMC3794877
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2013-0033
Advanced ultrasonography technologies to assess the effects of radiofrequency ablation on hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In RFA, ultrasonography (US) is most commonly used to guide tumor puncture, while its effects are assessed using dynamic computed tomography or magnetic resonance. The differences in modalities used for RFA and assessment of its effects complicate RFA. We developed a method for assessing the effects of RFA on HCC by combining contrast-enhanced (CE) US and real-time virtual sonography with three-dimensional US data.
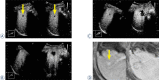
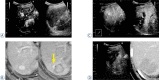
Patients and methods: Before RFA, we performed a sweep scan of the target HCC nodule and the surrounding hepatic parenchyma to generate three-dimensional US data. After RFA, we synchronized multi-planar reconstruction images derived from stored three-dimensional US data with real-time US images on the same US monitor and performed CEUS and real-time virtual sonography. Using a marking function, we drew a sphere marker along the target HCC nodule contour on pre-treatment US- multi-planar reconstruction images so that the automatically synchronized sphere marker represented the original HCC nodule contour on post-treatment real-time CEUS images. Ablation was considered sufficient when an avascular area with a margin of several millimeters in all directions surrounded the sphere marker on CEUS.
Results: This method was feasible and useful for assessing therapeutic effects in 13 consecutive patients with HCC who underwent RFA. In 2 patients who underwent multiple sessions of RFA, HCC-nodule portions requiring additional RFA were easily identified on US images.
Conclusions: This method using advanced US technologies will facilitate assessment of the effects of RFA on HCC.
Keywords: contrast-enhanced ultrasonography; hepatocellular carcinoma; radiofrequency ablation; real-time virtual sonography; three-dimensional ultrasonography.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Use of intra-procedural fusion imaging combining contrast-enhanced ultrasound using a perflubutane-based contrast agent and auto sweep three-dimensional ultrasound for guiding radiofrequency ablation and evaluating its efficacy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Hyperthermia. 2020;37(1):202-211. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2020.1729422. Int J Hyperthermia. 2020. PMID: 32070164
-
Planning Sonography Using Real-time Virtual Sonography and Contrast-enhanced Sonography for Radiofrequency Ablation of Inconspicuous Hepatocellular Carcinoma Nodules.Hepatogastroenterology. 2015 May;62(139):661-6. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 26897949
-
Pretreatment evaluation with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas with poor conspicuity on conventional ultrasonography.Korean J Radiol. 2013 Sep-Oct;14(5):754-63. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.5.754. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Korean J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24043968 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of the multimodality fusion imaging for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Dig Dis. 2012;30(6):580-7. doi: 10.1159/000343070. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Dig Dis. 2012. PMID: 23258098 Review.
-
Local ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in taiwan.Liver Cancer. 2013 Apr;2(2):73-83. doi: 10.1159/000343843. Liver Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24159599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Image Fusion System for Estimating the Therapeutic Effects of Radiofrequency Ablation on Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Radiol Oncol. 2017 Jul 18;51(3):263-269. doi: 10.1515/raon-2017-0028. eCollection 2017 Sep. Radiol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28959162 Free PMC article.
-
Bipolar radiofrequency ablation for liver tumors: comparison of contrast-enhanced ultrasound with contrast-enhanced MRI/CT in the posttreatment imaging evaluation.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Aug 15;7(9):6108-16. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25337258 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of percutaneous ultrasound guided radiofrequency ablation for treating cervical metastatic lymph nodes from papillary thyroid carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017 Aug;143(8):1555-1562. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2386-6. Epub 2017 Mar 24. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28342000 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous ultrasound-guided laser ablation for the treatment of cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis: a pilot study.J Int Med Res. 2019 Apr;47(4):1512-1520. doi: 10.1177/0300060518821818. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Int Med Res. 2019. PMID: 30632441 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic splenosis mimicking liver metastases in a patient with history of childhood immature teratoma.Radiol Oncol. 2016 Apr 23;50(2):212-7. doi: 10.2478/raon-2014-0040. eCollection 2016 Jun 1. Radiol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27247554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tiong L, Maddern GJ. Systematic review and meta-analysis of survival and disease recurrence after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg. 2011;98:1210–24. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs T, Kachelriess M, Kalender WA. Technical advances in multi-slice spiral CT. Eur J Radiol. 2000;36:69–73. - PubMed
-
- Kudo M. New sonographic techniques for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 2007;37(Suppl 2):S193–9. - PubMed
-
- Okamoto E, Sato S, Sanchez-Siles AA, Ishine J, Miyake T, Amano Y, et al. Evaluation of virtual CT sonography for enhanced detection of small hepatic nodules: a prospective pilot study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194:1272–8. - PubMed
-
- Minami Y, Kudo M, Chung H, Inoue T, Takahashi S, Hatanaka K, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of sonographically unidentifiable liver tumors. Feasibility and usefulness of a novel guiding technique with an integrated system of computed tomography and sonographic images. Oncology. 2007;72(Suppl 1):111–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
