The potential value of the neutral comet assay and γH2AX foci assay in assessing the radiosensitivity of carbon beam in human tumor cell lines
- PMID: 24133390
- PMCID: PMC3794881
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2013-0045
The potential value of the neutral comet assay and γH2AX foci assay in assessing the radiosensitivity of carbon beam in human tumor cell lines
Abstract
Background: Carbon ions ((12)C(6+)) are high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation characterized by higher relative biological effectiveness than low LET radiation. The assessment of tumour radiosensitivity would be particularly useful in optimizing the radiation dose during radiotherapy. The aim of the current study was to evaluate the potential value of the neutral comet assay and γH2AX foci assay in assessing (12)C(6+) radiosensitivity of tumour cells.
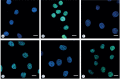
Materials and methods: The doses of (12)C(6+) and X-rays used in the present study were 2 and 4 Gy. The survival fraction, DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) and repair kinetics of DSB were assayed with clonogenic survival, neutral comet assay and γH2AX foci assay in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells, hepatoma HepG2 cells, and mucoepidermoid carcinoma MEC-1 cells at the time points of 0.5, 4, 16 and 24 h after (12)C(6+) and X-rays irradiation.
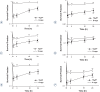
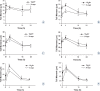
Results: The survival fraction for 12C6+ irradiation was much more inhibited than for X-rays (p < 0.05) in all three tumour cell lines tested. Substantial amounts of residual damage, assessed by the neutral comet assay, were present after irradiation (p < 0.05). The highest residual damage was observed at 0.5 or 4 h, both for (12)C(6+) and X-ray irradiation. However, the residual damage in HeLa and MEC-1 cells was higher for (12)C(6+) than X-rays (p < 0.05). The strongest induction of γH2AX foci was observed after 30 min, for all three tumour cell lines (p < 0.01). The franction of γH2AX foci persisted for at least 24 h after (12)C6+ irradiation; in HeLa cells and MEC-1 was higher than after X-ray irradiation (p < 0.05). The correlation coefficients between the clonogenic survival, neutral comet assay and γH2AX foci assay were not statistically significant, except for some tumour cells at individual irradiation doses and types.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated that the neutral comet assay and γ-H2AX foci assay could be used to assess the radiosensitivity of (12)C(6+) in human tumour cells.
Keywords: DNA double strand breaks; X-rays; carbon ions; human tumour cells; radiation sensitivity; γH2AX.
Figures


Similar articles
-
pATM and γH2AX are effective radiation biomarkers in assessing the radiosensitivity of 12C6+ in human tumor cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2017 Apr 26;17:49. doi: 10.1186/s12935-017-0419-5. eCollection 2017. Cancer Cell Int. 2017. PMID: 28450809 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of clonogenic cell survival and DNA damage induced by 188Re and X-rays in rat thyroid cells.Nuklearmedizin. 2017 Feb 14;56(1):47-54. doi: 10.3413/Nukmed-0842-16-08. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Nuklearmedizin. 2017. PMID: 27781237
-
Induction and persistence of large γH2AX foci by high linear energy transfer radiation in DNA-dependent protein kinase-deficient cells.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Nov 15;87(4):785-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.07.014. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 23972723
-
Assessing radiosensitivity through sublethal damage recovery: a comparison of survival-based and molecular repair kinetics.Phys Med Biol. 2025 Jun 16;70(12). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ade221. Phys Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40480255
-
Irradiation induced foci (IRIF) as a biomarker for radiosensitivity.Mutat Res. 2012 Aug 1;736(1-2):39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.05.017. Epub 2011 May 30. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 21651917 Review.
Cited by
-
The metabolomic profile of gamma-irradiated human hepatoma and muscle cells reveals metabolic changes consistent with the Warburg effect.PeerJ. 2016 Jan 26;4:e1624. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1624. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 26823999 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of selected anti-cancer drugs on the induction of DNA double-strand breaks and changes in gene expression in human hepatoma HepG2 cells.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Aug;23(15):14751-61. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5420-8. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26392091
-
Expression of the γ-phosphorylated histone H2AX in gastric carcinoma and gastric precancerous lesions.Oncol Lett. 2015 Apr;9(4):1790-1794. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.2896. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25789044 Free PMC article.
-
Pericytes augment glioblastoma cell resistance to temozolomide through CCL5-CCR5 paracrine signaling.Cell Res. 2021 Oct;31(10):1072-1087. doi: 10.1038/s41422-021-00528-3. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34239070 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Photon and Charged Particle Therapy Using DNA Damage Biomarkers.Int J Part Ther. 2018 Summer;5(1):15-24. doi: 10.14338/IJPT-18-00018.1. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Int J Part Ther. 2018. PMID: 31773017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nomiya T, Tsuji H, Hirasawa N, Kato H, Kamada T, Mizoe J, et al. Carbon ion radiation therapy for primary renal cell carcinoma: initial clinical experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;72:828–33. - PubMed
-
- Ogata T, Teshima T, Kagawa K, Hishikawa Y, Takahashi Y, Kawaguchi A, et al. Particle irradiation suppresses metastatic potential of cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:113–20. - PubMed
-
- Prise KM, Folkard M, Newman HC, Michael BD. Effect of radiation quality on lesion complexity in cellular DNA. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994;66:537–42. - PubMed
-
- Jayakumar S, Bhilwade HN, Pandey BN, Sandur SK, Chaubey RC. The potential value of the neutral comet assay and the expression of genes associated with DNA damage in assessing the radiosensitivity of tumor cells. Mutat Res. 2012;748:52–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
