Sense-antisense gene pairs: sequence, transcription, and structure are not conserved between human and mouse
- PMID: 24133500
- PMCID: PMC3783845
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00183
Sense-antisense gene pairs: sequence, transcription, and structure are not conserved between human and mouse
Abstract
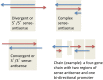
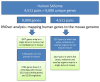
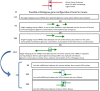
Previous efforts to characterize conservation between the human and mouse genomes focused largely on sequence comparisons. These studies are inherently limited because they don't account for gene structure differences, which may exist despite genomic sequence conservation. Recent high-throughput transcriptome studies have revealed widespread and extensive overlaps between genes, and transcripts, encoded on both strands of the genomic sequence. This overlapping gene organization, which produces sense-antisense (SAS) gene pairs, is capable of effecting regulatory cascades through established mechanisms. We present an evolutionary conservation assessment of SAS pairs, on three levels: genomic, transcriptomic, and structural. From a genome-wide dataset of human SAS pairs, we first identified orthologous loci in the mouse genome, then assessed their transcription in the mouse, and finally compared the genomic structures of SAS pairs expressed in both species. We found that approximately half of human SAS loci have single orthologous locations in the mouse genome; however, only half of those orthologous locations have SAS transcriptional activity in the mouse. This suggests that high human-mouse gene conservation overlooks widespread distinctions in SAS pair incidence and expression. We compared gene structures at orthologous SAS loci, finding frequent differences in gene structure between human and orthologous mouse SAS pair members. Our categorization of human SAS pairs with respect to mouse conservation of expression as well as structure points to limitations of mouse models. Gene structure differences, including at SAS loci, may account for some of the phenotypic distinctions between primates and rodents. Genes in non-conserved SAS pairs may contribute to evolutionary lineage-specific regulatory outcomes.
Keywords: bidirectional promoters; complex loci; evolution; expressed sequence tags (ESTs); long non-coding RNA (lncRNA); sense-antisense; transcriptome.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of cis-encoded antisense RNAs in eukaryotes.Gene. 2007 May 1;392(1-2):134-41. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.12.005. Epub 2006 Dec 13. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17250976
-
Complex Loci in human and mouse genomes.PLoS Genet. 2006 Apr;2(4):e47. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020047. Epub 2006 Apr 28. PLoS Genet. 2006. PMID: 16683030 Free PMC article.
-
Landscape of Overlapping Gene Expression in the Equine Placenta.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jul 2;10(7):503. doi: 10.3390/genes10070503. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31269762 Free PMC article.
-
Natural antisense transcripts.RNA Biol. 2005 Apr;2(2):53-62. doi: 10.4161/rna.2.2.1852. Epub 2005 Apr 19. RNA Biol. 2005. PMID: 17132938 Review.
-
Retrospective analysis: reproducibility of interblastomere differences of mRNA expression in 2-cell stage mouse embryos is remarkably poor due to combinatorial mechanisms of blastomere diversification.Mol Hum Reprod. 2018 Jul 1;24(7):388-400. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gay021. Mol Hum Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29746690
Cited by
-
Antisense-mediated regulation of exon usage in the elastic spring region of Titin modulates sarcomere function.Cardiovasc Res. 2025 May 6;121(4):629-642. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaf037. Cardiovasc Res. 2025. PMID: 40042822 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs in Atrial Fibrillation: Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes as a Model System.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 30;21(15):5424. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155424. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subclone Eradication Analysis Identifies Targets for Enhanced Cancer Therapy and Reveals L1 Retrotransposition as a Dynamic Source of Cancer Heterogeneity.Cancer Res. 2021 Oct 1;81(19):4901-4909. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0371. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34348967 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing vitamins on the long non-coding lane of the transcriptome: vitamin regulation of LncRNAs.Genes Nutr. 2024 Mar 12;19(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12263-024-00739-4. Genes Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38475720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neighboring gene regulation by antisense long non-coding RNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Feb 3;16(2):3251-66. doi: 10.3390/ijms16023251. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25654223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

