Bisebromoamide, an extract from Lyngbya species, induces apoptosis through ERK and mTOR inhibitions in renal cancer cells
- PMID: 24133625
- PMCID: PMC3797566
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.53
Bisebromoamide, an extract from Lyngbya species, induces apoptosis through ERK and mTOR inhibitions in renal cancer cells
Abstract
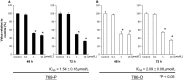
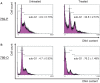
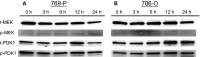
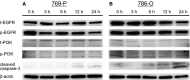
Advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) remains an incurable disease, and newer anticancer drugs are needed. Bisebromoamide, a novel cytotoxic peptide, was isolated from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya species at our laboratory in 2009. This compound specifically inhibited the phosphorylation of ERK in platelet-derived growth factor-activated normal rat kidney cells. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect and elucidate the potential mechanism of Bisebromoamide actions on human RCC cells. Two renal cancer cell lines, 769-P and 786-O, were used. The effects of Bisebromoamide were analyzed employing assays for water-soluble Tetrazolium-1 salts. Apoptosis was determined by flow cytometric TUNEL analysis. Cell-cycle distributions were analyzed by flow cytometry using BrdU/propidium iodide (PI) staining. Kinases of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target of Rapamycin (mTOR) pathway and Raf/MEK/ERK pathway were analyzed by Western blotting. After Bisebromoamide treatment for 48 and 72 h, cell viability was significantly decreased in both cell lines at 1 and 10 μmol/L. After treatment with 1 μmol/L Bisebromoamide for 72 h, apoptosis and the increased percentage of cells in the sub-G1 phase were observed in both cell lines. Bisebromoamide inhibited the phosphorylation of ERK and Akt in both cell lines tested. Similar effects were demonstrated for phosphorylation of mTOR and p70 S6. Bisebromoamide is a promising potential agent against RCC due to its ability to inhibit both the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways.
Keywords: Akt; Bisebromoamide; ERK; apoptosis; mTOR; renal cell carcinoma.
Figures



Similar articles
-
mTOR inhibition induces compensatory, therapeutically targetable MEK activation in renal cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 2;9(9):e104413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104413. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25180793 Free PMC article.
-
β-Elemene induces apoptosis in human renal-cell carcinoma 786-0 cells through inhibition of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt/ mTOR signalling pathways.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(6):2739-44. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.6.2739. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012. PMID: 22938451
-
The PI3K/Akt and mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathways in human uveal melanoma cells: interaction with B-Raf/ERK.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Jan;51(1):421-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3974. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19661225
-
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR inhibitors: rationale and importance to inhibiting these pathways in human health.Oncotarget. 2011 Mar;2(3):135-64. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.240. Oncotarget. 2011. PMID: 21411864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical pathways of oral squamous cell carcinoma: molecular biomarker and therapeutic intervention.Med Oncol. 2022 Jan 20;39(3):30. doi: 10.1007/s12032-021-01633-4. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35059897 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Small Peptides of Marine Origin in Cancer Therapy.Mar Drugs. 2021 Feb 19;19(2):115. doi: 10.3390/md19020115. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33669851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyanobacteria as Natural Therapeutics and Pharmaceutical Potential: Role in Antitumor Activity and as Nanovectors.Molecules. 2021 Jan 5;26(1):247. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010247. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33466486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SOX9 was involved in TKIs resistance in renal cell carcinoma via Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Apr 1;8(4):3871-81. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26097571 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally Inspired Peptide Leads: Alanine Scanning Reveals an Actin-Targeting Thiazole Analogue of Bisebromoamide.Chembiochem. 2016 Sep 2;17(17):1621-7. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201600257. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Chembiochem. 2016. PMID: 27304907 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK signaling pathway-targeted marine compounds in cancer therapy.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Jan;147(1):3-22. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03460-y. Epub 2021 Jan 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33389079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maira S. M., Stauffer F., Brueggen J., Furet P., Schnell C., Fritsch C. Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008;7:1851–1863. - PubMed
-
- Motzer R. J., Escudier B., Oudard S., Hutson T. E., Porta C., Bracarda S. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372:449–456. - PubMed
-
- Atkins M. B., Hidalgo M., Stadler W. M., Logan T. F., Dutcher J. P., Hudes G. R. Randomized phase II study of multiple dose levels of CCI-779, a novel mammalian target of rapamycin kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced refractory renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004;22:909–918. - PubMed
-
- Ratain M. J., Eisen T., Stadler W. M., Flaherty K. T., Kaye S. B., Rosner G. L. Phase II placebo-controlled randomized discontinuation trial of sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:2505–2512. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

