Estrogenic and mutagenic activities of Crotalaria pallida measured by recombinant yeast assay and Ames test
- PMID: 24134316
- PMCID: PMC3766270
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-216
Estrogenic and mutagenic activities of Crotalaria pallida measured by recombinant yeast assay and Ames test
Abstract
Background: Crotalaria pallida Ailton is a plant belonging to the Fabaceae family, popularly known as "rattle or rattlesnake" and used in traditional medicine to treat swelling of the joints and as a vermifuge. Previous pharmacological studies have also reported anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and antifungal activities. Nevertheless, scientific information regarding this species is scarce, and there are no reports related to its possible estrogenic and mutagenic effects. Thus, the purpose of the present study was to investigate the estrogenic potential of C. pallida leaves by means of the Recombinant Yeast Assay (RYA), seeking an alternative for estrogen replacement therapy during menopause; and to reflect on the safe use of natural products to assess the mutagenic activity of the crude extract from C. pallida leaves, the dichloromethane fraction and stigmasterol by means of the Ames test.
Methods: The recombinant yeast assay with the strain BY4741 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, was performed with the ethanolic extract, dichloromethane fraction and stigmasterol isolated from the leaves of C. pallida. Mutagenic activity was evaluated by the Salmonella/microsome assay (Ames test), using the Salmonella typhimurium tester strains TA100, TA98, TA97 and TA102, with (+S9) and without (-S9) metabolization, by the preincubation method.
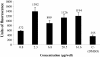
Results: All samples showed estrogenic activity, mainly stigmasterol. The ethanolic extract from C. pallida leaves showed mutagenic activity in the TA98 strain (-S9), whereas dichloromethane fraction and stigmasterol were found devoid of activity.
Conclusion: Considering the excellent estrogenic activity performed by stigmasterol in the RYA associated with the absence of mutagenic activity when evaluated by the Ames test, stigmasterol becomes a strong candidate to be used in hormone replacement therapy during menopause.
Figures

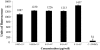

Similar articles
-
Estrogenic Activity of Coffee Constituents.Nutrients. 2019 Jun 21;11(6):1401. doi: 10.3390/nu11061401. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31234352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutagenicity and antimutagenicity of six Brazilian Byrsonima species assessed by the Ames test.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jun 5;14:182. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-182. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24898326 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro toxicological assessment of Arrabidaea brachypoda (DC.) Bureau: Mutagenicity and estrogenicity studies.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;90:29-35. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.08.010. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28823851
-
Estrogenic and chemopreventive activities of xanthones and flavones of Syngonanthus (Eriocaulaceae).Steroids. 2013 Nov;78(11):1053-63. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Steroids. 2013. PMID: 23891669
-
Mutagenic potential of medicinal plants evaluated by the Ames Salmonella/microsome assay: A systematic review.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020 Oct-Dec;786:108338. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2020.108338. Epub 2020 Oct 18. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 33339578
Cited by
-
A perspective review on factors that influence mutagenicity in medicinal plants and their health implications.Toxicol Sci. 2025 Apr 1;204(2):121-142. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaf004. Toxicol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39804670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogenic Activity of Coffee Constituents.Nutrients. 2019 Jun 21;11(6):1401. doi: 10.3390/nu11061401. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31234352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutagenicity and antimutagenicity of six Brazilian Byrsonima species assessed by the Ames test.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jun 5;14:182. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-182. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24898326 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic compounds and extracts from Crotalaria calycina Schrank potentially alleviate pain and inflammation through inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2: An in vivo and molecular dynamics studies.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 17;8(12):e12368. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12368. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36590510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Everist SL. Poisonous plants of Australia. Australia: Angus and Robertson Publishers; 1974. pp. 284–295.
-
- Jain SK, Borthakur SK. Etnobotany of the Mikers of India. Econ Bot. 1980;34(3):264–272. doi: 10.1007/BF02858646. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

