Vascular calcification in end-stage renal disease
- PMID: 24134325
- PMCID: PMC3813300
- DOI: 10.1111/hdi.12084
Vascular calcification in end-stage renal disease
Abstract
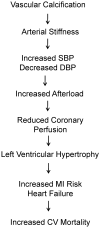
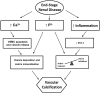
Vascular calcification is highly prevalent in end-stage renal disease and independently predictive of future cardiovascular events and mortality. Calcification can occur in both the intimal and medial layers of vasculature, but medial calcification is the major form in end-stage renal disease. Medial calcification increases large elastic artery stiffness and pulse-pressure, promotes left ventricular hypertrophy, reduces perfusion of the coronary arteries, and ultimately promotes increased cardiovascular mortality via increased risk of myocardial infarction and heart failure. It results not from a passive deposition of calcium and phosphate due to increased circulating levels, but rather is an active cell-mediated process involving vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis and vesicle release, a shift in the balance of inhibitors and promoters of vascular calcification, and vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation from a contractile to osteochondrogenic phenotype. This phenotypic shift requires phosphate, as well as the uptake of phosphate by the sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter PiT-1, which is upregulated by proinflammatory cytokines and the uremic milieu. Further research is needed to determine if targeting these processes can ultimately reduce vascular calcification in this high cardiovascular risk population.
Keywords: Calcium; end-stage renal disease; phosphate; vascular calcification.
© 2013 The Authors. Hemodialysis International © 2013 International Society for Hemodialysis.
Figures
References
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS. Cardiovascular disease and mortality in ESRD. Journal of nephrology. 1998;11:239–245. - PubMed
-
- Verberckmoes SC, Persy V, Behets GJ, et al. Uremia-related vascular calcification: more than apatite deposition. Kidney international. 2007;71:298–303. - PubMed
-
- Goodman WG, Goldin J, Kuizon BD, et al. Coronary-artery calcification in young adults with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing dialysis. The New England journal of medicine. 2000;342:1478–1483. - PubMed
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. American journal of kidney diseases: the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation. 1998;32:S112–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

