Drug resistance profile and biofilm forming potential of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from contact lenses in Karachi-Pakistan
- PMID: 24134792
- PMCID: PMC3852958
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2415-13-57
Drug resistance profile and biofilm forming potential of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from contact lenses in Karachi-Pakistan
Abstract
Background: The contaminated contact lens provides Pseudomonas aeruginosa an ideal site for attachment and biofilm production. Continuous contact of the eye to the biofilm-infested lens can lead to serious ocular diseases, such as keratitis (corneal ulcers). The biofilms also prevent effective penetration of the antibiotics, which increase the chances of antibiotic resistance.
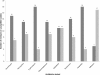
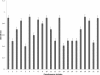
Methods: For this study, 22 Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were obtained from 36 contact lenses and 14 contact lens protective fluid samples. These isolates were tested against eight commonly used antibiotics using Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method. The biofilm forming potential of these isolates was also evaluated using various qualitative and quantitative techniques. Finally, a relationship between biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance was also examined.
Results: The isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa tested were found resistant to most of the antibiotics tested. Qualitative and quantitative biofilm analysis revealed that most of the isolates exhibited strong biofilm production. The biofilm production was significantly higher in isolates that were multi-drug resistant (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Our study indicates that multi-drug resistant, biofilm forming Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates are mainly involved in contact lens associated infections. This appears to be the first report from Pakistan, which analyzes both antibiotic resistance profile and biofilm forming potential of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from contact lens of the patients with contact lens associated infections.
Figures

References
-
- Gales AC, Sader HH, Jones RN. Respiratory tract pathogens isolated from patients hospitalized with suspected pneumonia in Latin America: frequency of occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility profile: results from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (1997–2000) Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2002;44(3):301–311. doi: 10.1016/S0732-8893(02)00499-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Drago L. Bacteria and biofilm in respiratory tract infections. Infez Med. 2009;2(17):3–9. - PubMed
-
- Chi H, Chang KY, Chang HC, Chiu NC, Huang FY. Infections associated with indwelling ventriculostomy catheters in a teaching hospital. Int J Infect Dis. 2009;14(3):e216–219. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

