Iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) control in India
- PMID: 24135192
- PMCID: PMC3818611
Iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) control in India
Abstract
Iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) constitute the single largest cause of preventable brain damage worldwide. Majority of consequences of IDD are invisible and irreversible but at the same time these are preventable. In India, the entire population is prone to IDD due to deficiency of iodine in the soil of the subcontinent and consequently the food derived from it. To combat the risk of IDD, salt is fortified with iodine. However, an estimated 350 million people do not consume adequately iodized salt and, therefore, are at risk for IDD. Of the 325 districts surveyed in India so far, 263 are IDD-endemic. The current household level iodized salt coverage in India is 91 per cent with 71 per cent households consuming adequately iodized salt. The IDD control goal in India was to reduce the prevalence of IDD below 10 per cent in the entire country by 2012. What is required is a "mission approach" with greater coordination amongst all stakeholders of IDD control efforts in India. Mainstreaming of IDD control in policy making, devising State specific action plans to control IDD, strict implementation of Food Safety and Standards (FSS) Act, 2006, addressing inequities in iodized salt coverage (rural-urban, socio-economic), providing iodized salt in Public Distribution System, strengthening monitoring and evaluation of IDD programme and ensuring sustainability of IDD control activities are essential to achieve sustainable elimination of IDD in India.
Figures





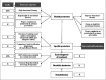
References
-
- New Delhi: Micronutrient Initiative; 2009. [accessed on July 1, 2011]. Micronutrient Initiative. Investing in the future - a united call to action on vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Global report, 2009. Available from: http://www.unitedcalltoaction.org/documents/Investing_in_the_future.pdf .
-
- Hetzel BS, Delange F, Dunn JT, Ling J, Mannar Venkatesh, Pandav CS, editors. International Council for the Control of Iodine Deficiency Disorders. New Delhi: Oxford University Press; 2004. [accessed on July 1, 2011]. Towards the global elimination of brain damage due to iodine deficiency - a global program for human development with a model applicable to a variety of health, social and environmental problems. Available from: http://www.iccidd.org/cm_data/hetzel-a-frontpage.pdf .
-
- Geneva: World Health Organization; 2007. ICCIDD, UNICEF, WHO. Assessment of iodine deficiency disorders and monitoring their elimination: a guide for programme managers.
-
- Bleichrodt N, Born MP. A meta-analysis of research on iodine and its relationship to cognitive development. In: Stanbury JB, editor. The damaged brain of iodine deficiency - Cognitive behavioral, neuromotor, educative aspects. New York: Cognizant Communication Corporation; 1994. pp. 195–200.
-
- New York: Nutrition Section, Programme Division United Nations Plaza; 2008. UNICEF. Sustainable Elimination of Iodine Deficiency; Progress since the 1990 World Summit for Children.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
