Chemotherapy-mediated p53-dependent DNA damage response in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: role of the mTORC1/2 and hypoxia-inducible factor pathways
- PMID: 24136229
- PMCID: PMC3920935
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.395
Chemotherapy-mediated p53-dependent DNA damage response in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: role of the mTORC1/2 and hypoxia-inducible factor pathways
Abstract
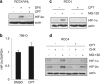
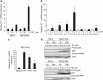
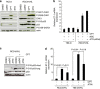
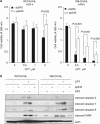
The DNA-damaging agent camptothecin (CPT) and its analogs demonstrate clinical utility for the treatment of advanced solid tumors, and CPT-based nanopharmaceuticals are currently in clinical trials for advanced kidney cancer; however, little is known regarding the effects of CPT on hypoxia-inducible factor-2α (HIF-2α) accumulation and activity in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Here we assessed the effects of CPT on the HIF/p53 pathway. CPT demonstrated striking inhibition of both HIF-1α and HIF-2α accumulation in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)-defective ccRCC cells, but surprisingly failed to inhibit protein levels of HIF-2α-dependent target genes (VEGF, PAI-1, ET-1, cyclin D1). Instead, CPT induced DNA damage-dependent apoptosis that was augmented in the presence of pVHL. Further analysis revealed CPT regulated endothelin-1 (ET-1) in a p53-dependent manner: CPT increased ET-1 mRNA abundance in VHL-defective ccRCC cell lines that was significantly augmented in their VHL-expressing counterparts that displayed increased phosphorylation and accumulation of p53; p53 siRNA suppressed CPT-induced increase in ET-1 mRNA, as did an inhibitor of ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) signaling, suggesting a role for ATM-dependent phosphorylation of p53 in the induction of ET-1. Finally, we demonstrate that p53 phosphorylation and accumulation is partially dependent on mTOR activity in ccRCC. Consistent with this result, pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1/2 kinase inhibited CPT-mediated ET-1 upregulation, and p53-dependent responses in ccRCC. Collectively, these data provide mechanistic insight into the action of CPT in ccRCC, identify ET-1 as a p53-regulated gene and demonstrate a requirement of mTOR for p53-mediated responses in this tumor type.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Suppressive effects of iron chelation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and their dependency on VHL inactivation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Mar;133:295-309. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.12.013. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30553971 Free PMC article.
-
VHL missense mutations in the p53 binding domain show different effects on p53 signaling and HIFα degradation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):10199-10212. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14372. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28052007 Free PMC article.
-
Prolyl hydroxylase 2 dependent and Von-Hippel-Lindau independent degradation of Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and 2 alpha by selenium in clear cell renal cell carcinoma leads to tumor growth inhibition.BMC Cancer. 2012 Jul 17;12:293. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-293. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22804960 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia, Hypoxia-inducible Transcription Factors, and Renal Cancer.Eur Urol. 2016 Apr;69(4):646-657. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.08.007. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 26298207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of PI3K signalling pathway in clear cell renal cell carcinoma in relation to VHL and HIF status.J Clin Pathol. 2021 Apr;74(4):216-222. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206693. Epub 2020 May 28. J Clin Pathol. 2021. PMID: 32467322 Review.
Cited by
-
Translational and HIF-1α-Dependent Metabolic Reprogramming Underpin Metabolic Plasticity and Responses to Kinase Inhibitors and Biguanides.Cell Metab. 2018 Dec 4;28(6):817-832.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Cell Metab. 2018. PMID: 30244971 Free PMC article.
-
ATM may be a protective factor in endometrial carcinogenesis with the progesterone pathway.Tumour Biol. 2015 Mar;36(3):1529-37. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2712-4. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25608836
-
HDAC 1 and 6 modulate cell invasion and migration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2016 Aug 9;16:617. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2604-7. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27506904 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for E3-ubiquitin ligase inhibitors: challenges and opportunities.Oncotarget. 2014 Sep 30;5(18):7988-8013. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2431. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25237759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying potential risk genes for clear cell renal cell carcinoma with deep reinforcement learning.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 15;16(1):3591. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58439-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40234405 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

