Tpo1-mediated spermine and spermidine export controls cell cycle delay and times antioxidant protein expression during the oxidative stress response
- PMID: 24136413
- PMCID: PMC3981086
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2013.165
Tpo1-mediated spermine and spermidine export controls cell cycle delay and times antioxidant protein expression during the oxidative stress response
Abstract
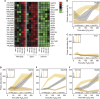
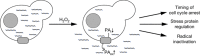
Cells counteract oxidative stress by altering metabolism, cell cycle and gene expression. However, the mechanisms that coordinate these adaptations are only marginally understood. Here we provide evidence that timing of these responses in yeast requires export of the polyamines spermidine and spermine. We show that during hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) exposure, the polyamine transporter Tpo1 controls spermidine and spermine concentrations and mediates induction of antioxidant proteins, including Hsp70, Hsp90, Hsp104 and Sod1. Moreover, Tpo1 determines a cell cycle delay during adaptation to increased oxidant levels, and affects H2O2 tolerance. Thus, central components of the stress response are timed through Tpo1-controlled polyamine export.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characteristics of the polyamine transporter TPO1 and regulation of its activity and cellular localization by phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 11;280(10):9646-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410274200. Epub 2005 Jan 6. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15637075
-
Yeast response and tolerance to benzoic acid involves the Gcn4- and Stp1-regulated multidrug/multixenobiotic resistance transporter Tpo1.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;101(12):5005-5018. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8277-6. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28409382 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae efflux pump Tpo1 rescues an Imp2 transcription factor-deficient mutant from bleomycin toxicity.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2014 Jul;55(6):518-24. doi: 10.1002/em.21865. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2014. PMID: 24599794
-
The response to heat shock and oxidative stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2012 Apr;190(4):1157-95. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.128033. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22209905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of cellular polyamine transport in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010 Jul;48(7):506-12. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.01.017. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20159658 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Stress on Biological Characteristics and Metabolism of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells of Deciduous Teeth.Int Dent J. 2025 Apr;75(2):908-920. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.09.011. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 39370340 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of MCHM on yeast metabolism.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 17;14(10):e0223909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223909. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31622418 Free PMC article.
-
The role of NAD and NAD precursors on longevity and lifespan modulation in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biogerontology. 2022 Apr;23(2):169-199. doi: 10.1007/s10522-022-09958-x. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Biogerontology. 2022. PMID: 35260986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Putrescine biosynthesis and export genes are essential for normal growth of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli.BMC Microbiol. 2018 Dec 27;18(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1355-9. BMC Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30587122 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Non-Enzymatic Reactions and Enzyme Promiscuity on Cellular Metabolism during (Oxidative) Stress Conditions.Biomolecules. 2015 Sep 10;5(3):2101-22. doi: 10.3390/biom5032101. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 26378592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Veal EA, Day AM, Morgan BA (2007) Hydrogen peroxide sensing and signaling. Mol Cell 26: 1–14 - PubMed
-
- Reth M (2002) Hydrogen peroxide as second messenger in lymphocyte activation. Nat Immunol 3: 1129–1134 - PubMed
-
- Sies H (1997) Oxidative stress: oxidants and antioxidants. Exp Physiol 82: 291–295 - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144: 646–674 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

