Correlation between fractional anisotropy and motor outcomes in one-year-old infants with periventricular brain injury
- PMID: 24136687
- PMCID: PMC4340685
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.24256
Correlation between fractional anisotropy and motor outcomes in one-year-old infants with periventricular brain injury
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether motor outcomes of an exercise intervention beginning at 2 months corrected age (CA) in children with periventricular brain injury (PBI) are correlated with fractional anisotropy (FA) measures derived from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) at 12 months CA.
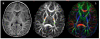
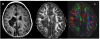
Materials and methods: DTI was performed in eight infants with PBI who were randomly assigned to kicking and treadmill stepping exercise or a no-training condition. Development was assessed using the Alberta Infant Motor Scale (AIMS) and the Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS). FA values were derived from regions of interest (ROIs) in the middle third of the posterior limb of the internal capsule (PLIC) and the posterior thalamic radiation (PTR).
Results: Significant correlations were observed between motor development and FA measures. For PLIC, the correlation coefficients were 0.82 between FA and AIMS, and -0.92 between FA and GMFCS, while for PTR the corresponding correlation coefficients were 0.73 and -0.80, respectively.
Conclusion: Results of this study suggest that quantitative evaluation of white matter tracts using DTI at 12 months CA may be useful for assessment of brain plasticity in children.
Keywords: DTI; fractional anisotropy (FA); infants; periventricular brain injury; treadmill exercise.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
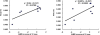
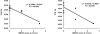
Similar articles
-
Early Diagnosis of Spastic Cerebral Palsy in Infants with Periventricular White Matter Injury Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Jan;40(1):162-168. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5914. Epub 2018 Dec 13. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019. PMID: 30545838 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging-based assessment of white matter tracts and visual-motor outcomes in very preterm neonates.Neuroradiology. 2016 Mar;58(3):301-10. doi: 10.1007/s00234-015-1625-2. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Neuroradiology. 2016. PMID: 26687071
-
Brain microstructural development at near-term age in very-low-birth-weight preterm infants: an atlas-based diffusion imaging study.Neuroimage. 2014 Feb 1;86:244-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.09.053. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24091089 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging study of pediatric patients with congenital hydrocephalus: 1-year postsurgical outcomes.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016 Sep;18(3):306-19. doi: 10.3171/2016.2.PEDS15628. Epub 2016 May 20. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27203134 Free PMC article.
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging and fractional anisotropy in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a literature review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E12. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16192. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581308 Review.
Cited by
-
Normal-appearing cerebral white matter in healthy adults: mean change over 2 years and individual differences in change.Neurobiol Aging. 2015 May;36(5):1834-48. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Neurobiol Aging. 2015. PMID: 25771392 Free PMC article.
-
Behavior During Tethered Kicking in Infants With Periventricular Brain Injury.Pediatr Phys Ther. 2015 Winter;27(4):403-12. doi: 10.1097/PEP.0000000000000173. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2015. PMID: 26397087 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
White matter lesions and DTI metrics related to various types of dysfunction in cerebral palsy: A meta-analysis and systematic review.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 24;20(1):e0312378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312378. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39854387 Free PMC article.
-
Brain structural connectivity increases concurrent with functional improvement: evidence from diffusion tensor MRI in children with cerebral palsy during therapy.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Jan 9;7:315-24. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.01.002. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 25610796 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- de Kieviet JF, Piek JP, Aarnoudse-Moens CS, Oosterlaan J. Motor Development in Very Preterm and Very Low-Birth-Weight Children From Birth to Adolescence A Meta-analysis. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association. 2009;302(20):2235–2242. - PubMed
-
- Back SA. Perinatal white matter injury: The changing spectrum of pathology and emerging insights into pathogenetic mechanisms. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews. 2006;12(2):129–140. - PubMed
-
- Roze E, Van Braeckel KNJA, van der Veere CN, Maathuis CGB, Martijn A, Bos AF. Functional Outcome at School Age of Preterm Infants With Periventricular Hemorrhagic Infarction. Pediatrics. 2009;123(6):1493–1500. - PubMed
-
- Hoon AH, Lawrie WT, Melhem ER, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of periventricular leukomalacia shows affected sensory cortex white matter pathways. Neurology. 2002;59(5):752–756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

